Key concepts
This page explains the concepts of the primary resources in the Data Catalog service—Catalogs, Databases, Tables, and Crawlers—along with the status and lifecycle of each resource.
Catalog
In Data Catalog, a catalog is a metadata namespace that organizes and separates table and database metadata. It serves as a metastore, allowing analysis engines such as Spark, Trino, and Hive to query and manage table metadata. Each catalog operates independently and does not share metadata. Additionally, all catalogs are provided with a High Availability (HA) architecture to ensure stable service operation.
KakaoCloud provides two types of catalogs: Standard and Iceberg.
Standard catalog
This is the default (Standard) catalog type, compatible with the Apache Hive Metastore.
- It can be created by specifying a particular VPC (subnet).
- You can store, modify, and delete metadata, such as table definitions and storage paths for the data you own, within the catalog.
Iceberg catalog
Apache Iceberg is an open table format designed for managing large-scale analytical data as reliably as a single SQL table. It is engineered to allow multiple engines (e.g., Spark, Trino) to safely read and write to the same table simultaneously.
- SQL-friendly operations: Express row-level changes through standard SQL (DML/DDL) and access data across multiple engines using a common format. (Implementation support may vary by engine).
- Schema and partition evolution: Columns can be added, renamed, or deleted, and partition layouts can be updated without recreating the table.
- Hidden partitioning: Partition transformations like
day(ts)orbucket(id)are managed as metadata, eliminating the need to manage physical directory structures manually. - Time travel and rollback: Every write operation automatically creates a snapshot, allowing users to query data or revert to a specific point in time or snapshot. (Availability varies by engine).
- Operational optimization (Compaction, etc.): Scan performance is improved and metadata overhead is reduced through file layout optimization features, such as merging small files.
The Data Catalog service registers and manages metadata such as Iceberg table schemas, partition transformations, and snapshots.
Actual query execution is performed by analysis engines like Spark or Trino. When configuring the engine, you must specify the REST catalog URI and the Warehouse (Object Storage) path.
- Format version: Provided based on Iceberg v2. While viewing and creating v1 tables is possible, some features may be limited.
- Catalog creation limit: Only one Iceberg catalog can be created per project (or account).
- Object Storage integration: We recommend using General Buckets (S3-compatible). Classic Buckets and Swift methods are not supported.
Database
A database in Data Catalog is a metadata container that logically groups tables. Its scope of support depends on the type of its parent catalog.
- A single table must belong to exactly one database.
- Databases are managed at the project level, and all databases registered in the project can be viewed in the console.
- Supported types:
- Standard type database: Databases based on the Hive data format.
- Iceberg type database: Databases based on the Iceberg data format.
Table
In Data Catalog, a table is a metadata entity that represents data in a data store. You can create tables in the KakaoCloud Console, and the metadata values are displayed in the console's table list.
- A table includes sub-metadata such as schema, partitions, and table properties.
- Tables can be created manually, and table information can be modified.
- If using Data Catalog as a metastore for a Hadoop ecosystem, metadata for migrated tables can also be modified.
- Behavioral differences by type:
- Standard type table: Hive-based tables supporting file formats such as Avro, JSON, Parquet, ORC, CSV, and TEXT; queried via engines like Hive or Trino.
- Iceberg type table: Iceberg table format supporting formats like Avro, Parquet, and ORC, while providing unique Iceberg features.
Crawler
In Data Catalog, a crawler is a feature that simplifies data discovery by scanning MySQL data to extract metadata and automatically updating the Data Catalog. You can create crawlers in the KakaoCloud Console, and table values generated by the crawler will appear in the table list.
- Schemas extracted by the crawler are stored in Data Catalog tables. Table names are formatted as: Prefix + MySQL Database Name_Table Name.
- Crawler execution history is displayed for up to 90 days; history older than 90 days is automatically deleted.
- You can set crawler execution intervals via a schedule.
- Crawler support type: The crawler feature is not supported in Iceberg catalogs.
Resource status and lifecycle
The resources for which status can be checked in Data Catalog are Catalogs, Databases, Tables, and Crawlers. You can determine the current operational state through the resource status.
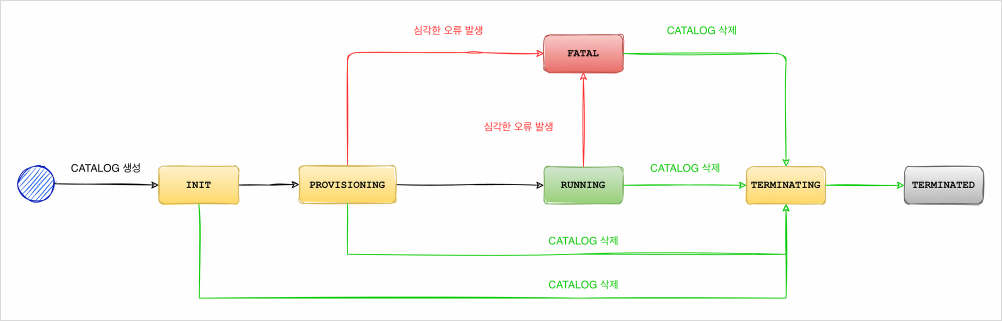 Catalog lifecycle
Catalog lifecycle
Catalog status
Standard type
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
INIT | Status immediately after the Standard catalog is created. |
PROVISIONING | Status while the VM for the Standard catalog is being created. |
RUNNING | The Standard catalog is running and available for use. |
PENDING | Status while the Standard catalog is performing a failover to recover from an error. |
FATAL | An error has occurred in the Standard catalog, making it unrecoverable. |
TERMINATING | Status while hardware resources are being returned to terminate the Standard catalog. |
TERMINATED | The Standard catalog has been terminated and is no longer available. |
Iceberg type
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
RUNNING | The Iceberg catalog is running and available for use. |
FATAL | An error has occurred in the Iceberg catalog, making it unrecoverable. |
TERMINATED | The Iceberg catalog has been terminated and is no longer available. |
Database and table status
The status of databases and tables is managed by create, modify, and delete operations. These statuses affect resource operations. A table possesses its own status but is also influenced by the status of its parent database. For example, a table can only be created or modified if the database is in the ACTIVE or ALTERING state.
💡 The status definitions for Standard type and Iceberg type databases and tables are identical.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
CREATING | Database or Table is being created. |
ALTERING | Database or Table is being modified. |
DELETING | Database or Table is being deleted. |
ACTIVE | Database or Table is available for use. |
INACTIVE | Database or Table is unavailable. |
Crawler status
Crawlers change states based on creation, modification, execution, and deletion operations. They are also affected by the status of the database and the source MySQL instance. For example, a crawler can only be created or run if the MySQL status is Available.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
CREATING | Crawler is being created. |
ALTERING | Crawler is being modified. |
DELETING | Crawler is being deleted. |
ACTIVE | The crawler configuration is active. |
RUNNING | Crawler is currently executing. |
INACTIVE | Crawler is unavailable (e.g., if the associated database is deleted). History remains viewable. |