Key Concepts
KakaoCloud's Hadoop Eco is a cloud platform service for executing distributed processing tasks using open-source frameworks such as Hadoop, Hive, HBase, Spark, Trino, and Kafka. It provides provisioning services for Hadoop, HBase, Trino, and Dataflow using KakaoCloud's Virtual Machines. The key concepts of the Hadoop Eco service are as follows:
Cluster
A cluster is a set of nodes provisioned using Virtual Machines.
Cluster bundles
Hadoop Eco provides Core Hadoop, HBase, Trino, Dataflow, and Custom bundles.
| Bundle | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Hadoop | Hadoop, Hive, Spark, and Tez are installed. - Data is stored in HDFS and analyzed using Hive and Spark. |
| HBase | Hadoop and HBase are installed. - Data is stored in HDFS and NoSQL services are provided using HBase. |
| Trino | Hadoop, Trino, Hive, and Tez are installed. - Data is stored in HDFS and analyzed using Trino and Hive. |
| Dataflow | Hadoop, Kafka, Druid, and Superset are installed. - Data is collected via Kafka and analyzed using Druid and Superset. |
| Custom | Hadoop and Zookeeper are installed by default, and users can freely select additional components to install. - Changing components in other bundles automatically switches them to a Custom bundle. |
Cluster availability types
To ensure operational stability, Hadoop Eco provides Standard (Single) and High Availability (HA) types.
| Availability Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Standard (Single) | Consists of 1 Master node and multiple Worker nodes. - Since there is only one Master node, HDFS and YARN may fail to operate if a fault occurs. |
| High Availability (HA) | Consists of 3 Master nodes and multiple Worker nodes. - HDFS and YARN are configured for HA, automatically recovering the Master in case of failure. |
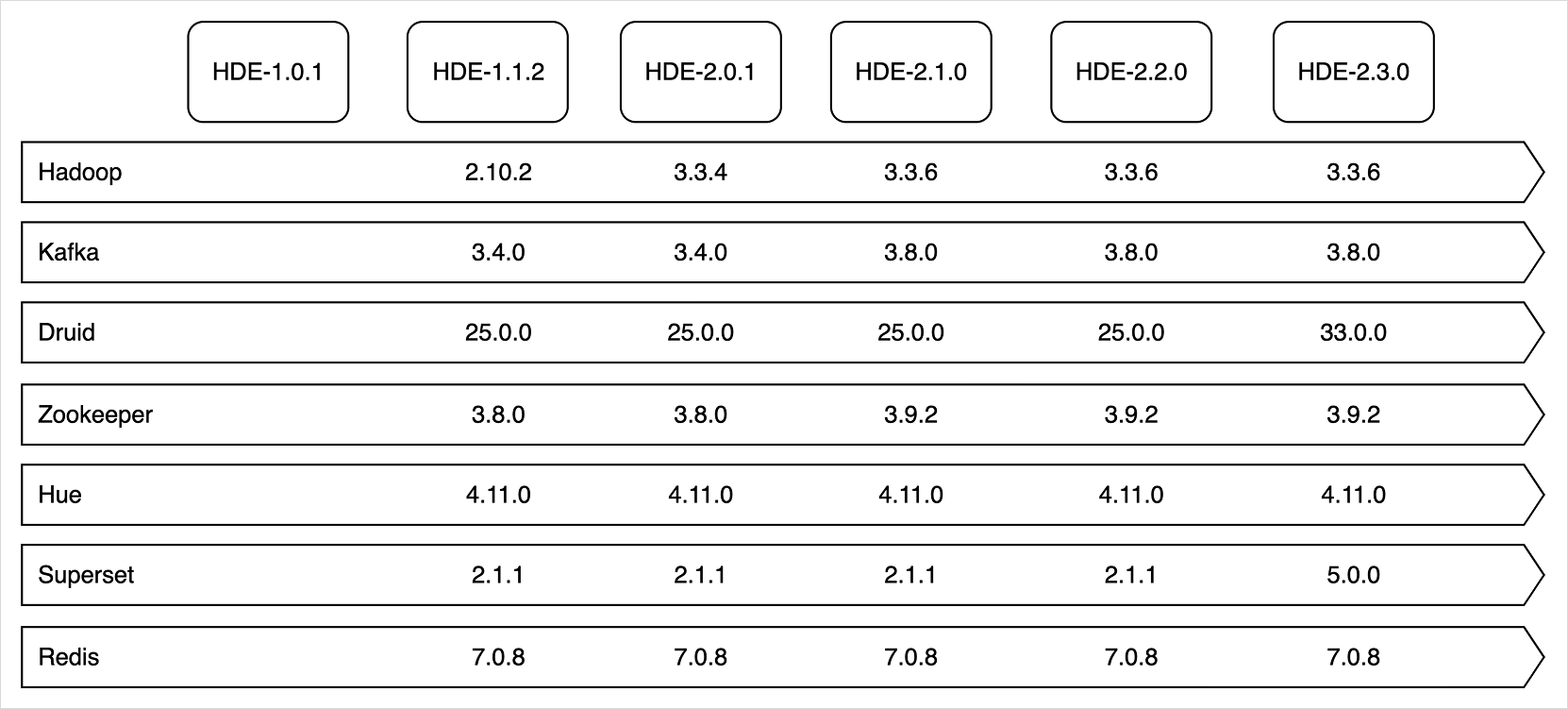
Cluster versions
The installed component versions are determined by the Hadoop Eco version. HDE clusters offer the Core Hadoop bundle for data analysis, the HBase bundle for HDFS-based NoSQL services, and starting from HDE version 1.1.2, Trino and Dataflow bundles are available. HDE version 2.0.1 supports Hadoop 3.x, HBase 2.x, and Hive 3.x.
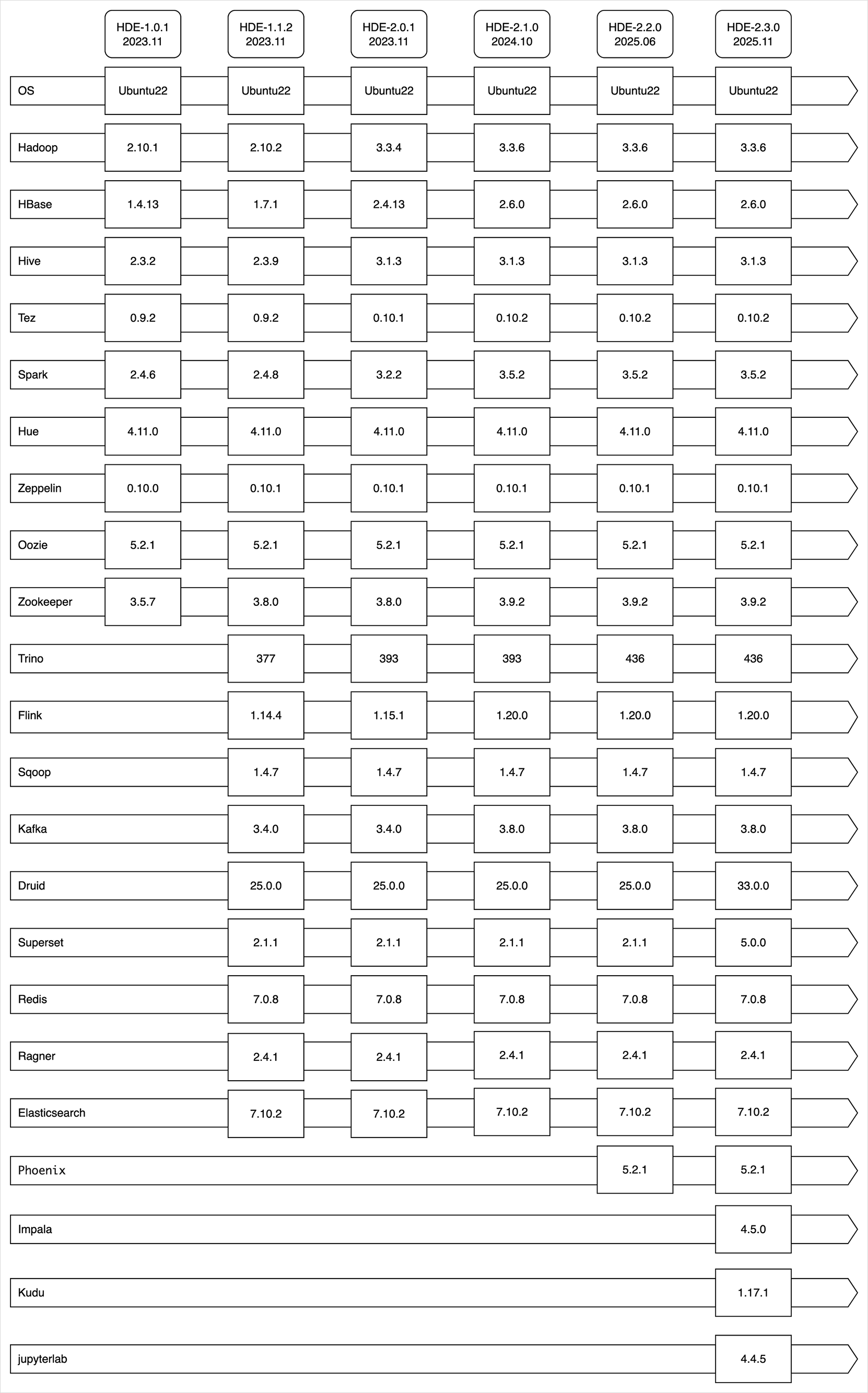
Components installed by bundle per cluster version
- Core Hadoop
- HBase
- Trino
- Dataflow
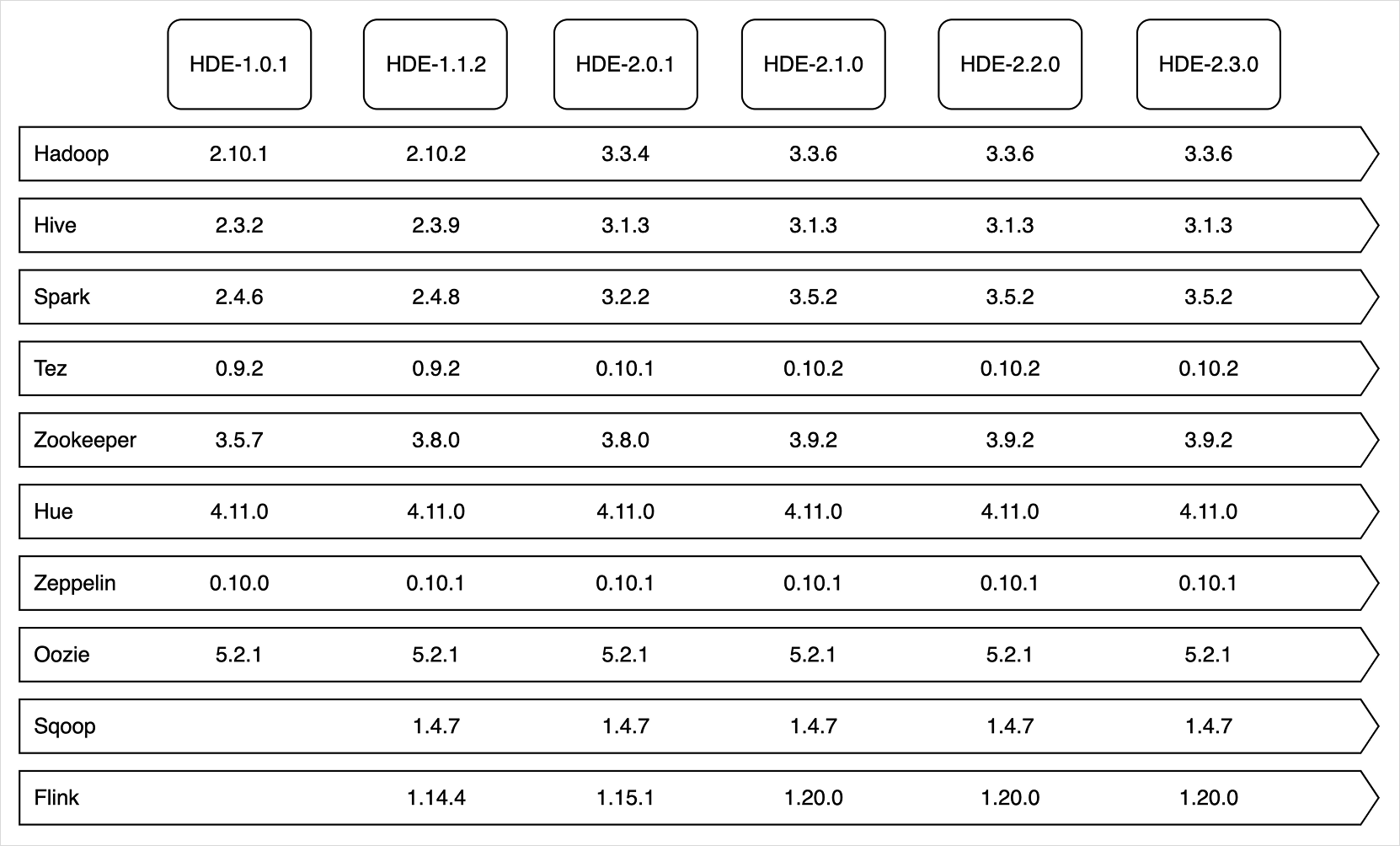 Core Hadoop
Core Hadoop
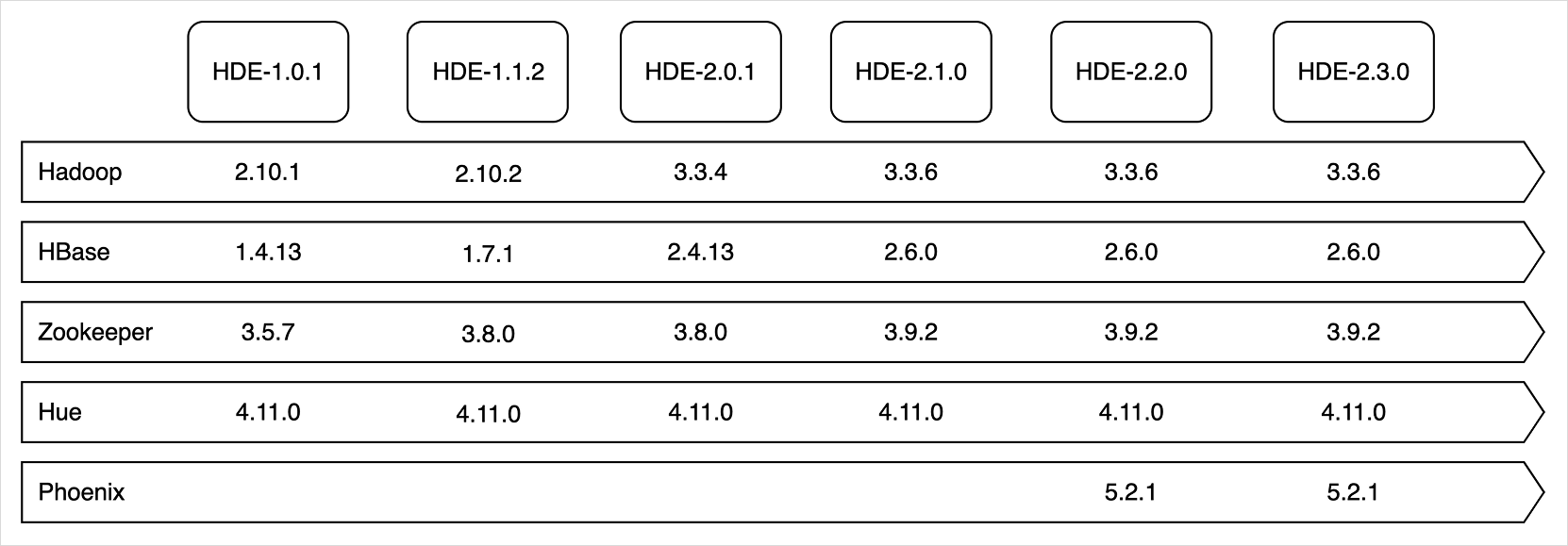 HBase
HBase
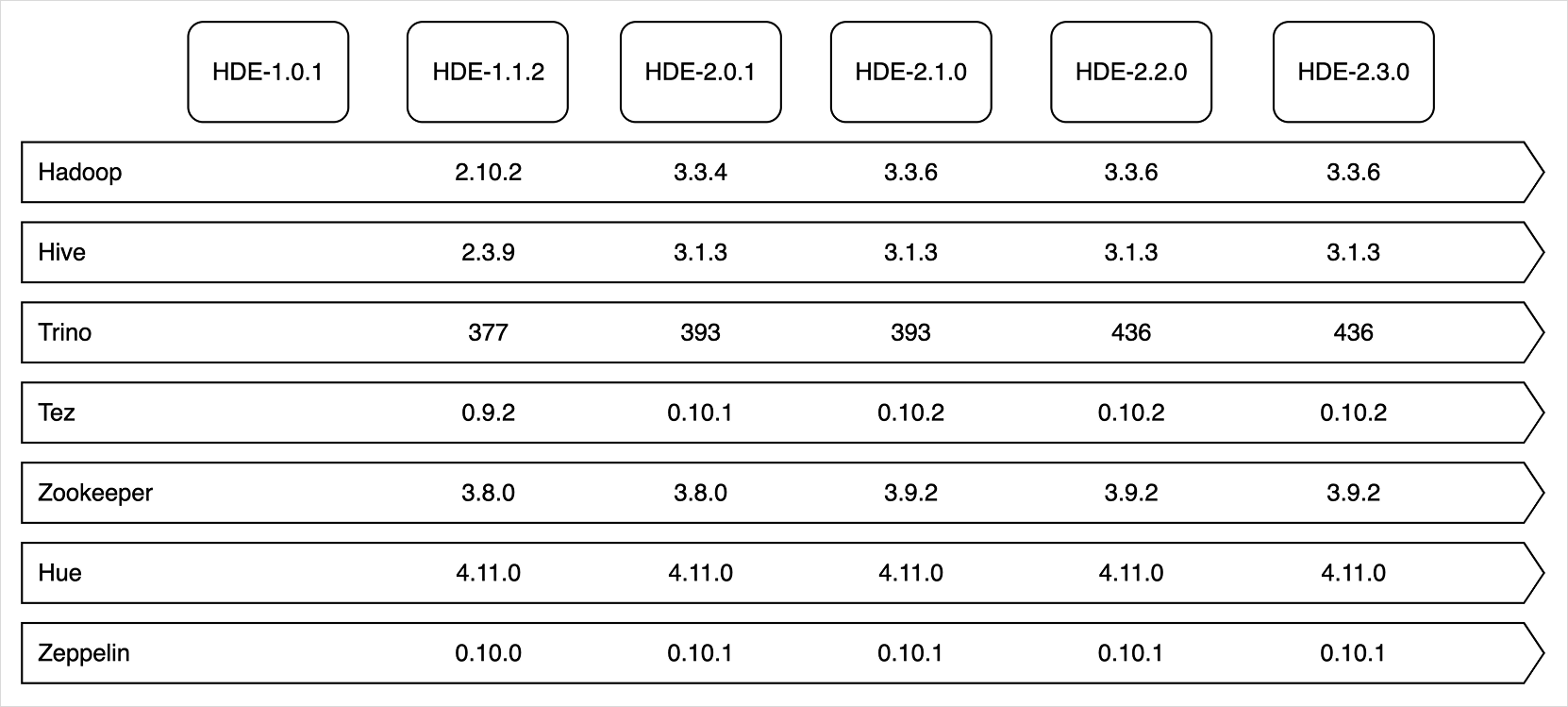 Trino
Trino
 Dataflow
Dataflow
Cluster lifecycle
Hadoop Eco clusters have various states and lifecycles, allowing you to check operational and task status and perform management functions. The lifecycle represents states such as installation, operation, and deletion after the initial creation request. Depending on how the user operates the cluster, the statuses of the cluster and its instances may differ.
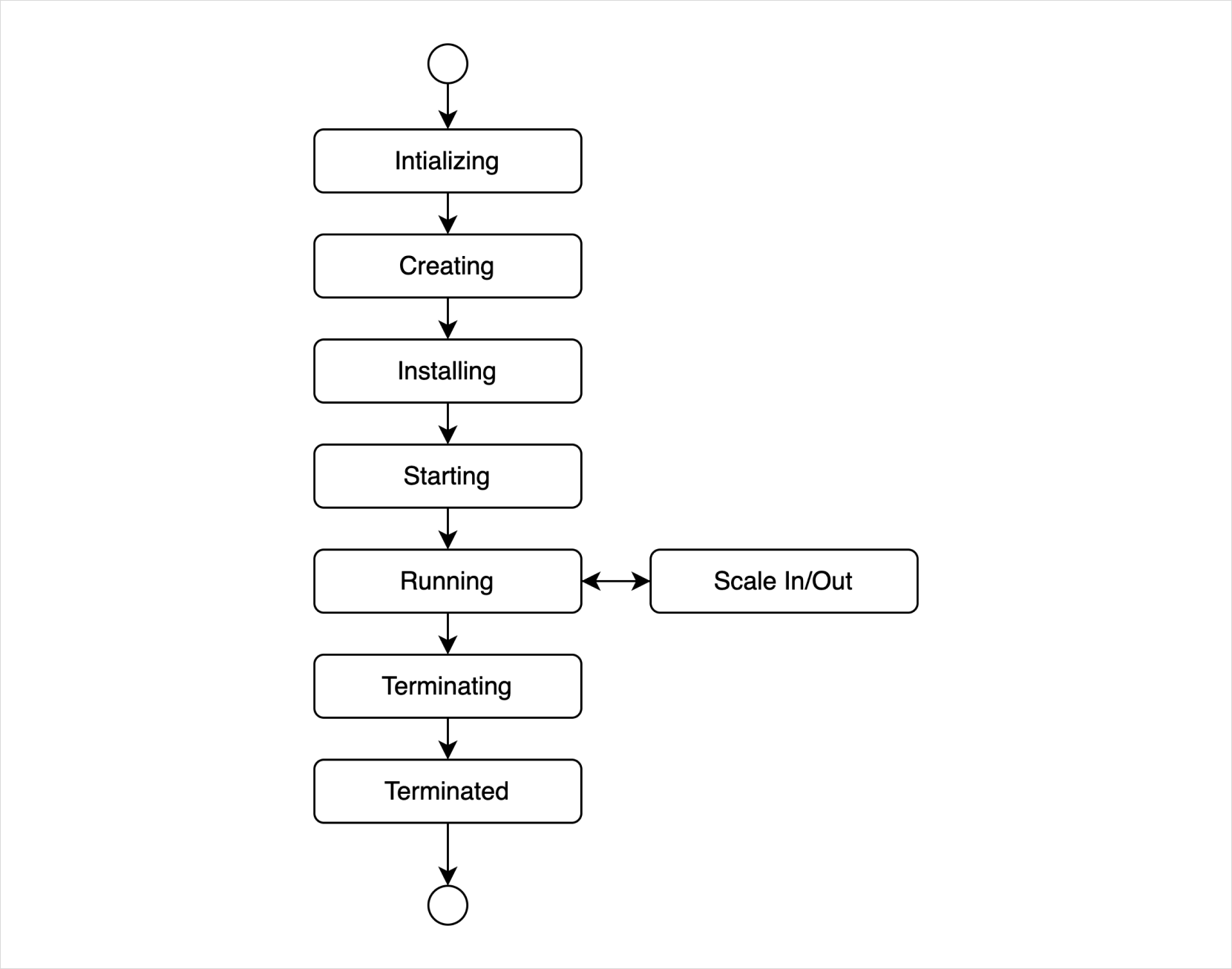 Cluster Lifecycle
Cluster Lifecycle
Cluster and Node Status
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
Initializing | User request meta-information is stored, and VM creation has been requested. |
Creating | VMs are being created. |
Installing | Hadoop Eco components are being installed on the created VMs. |
Starting | Hadoop Eco components are being executed. |
Running | All components are running, and the cluster is in operation. |
Running(Scale out initializing) | VM creation has been requested due to a cluster expansion request. |
Running(Scale out creating) | VMs are being created. |
Running(Scale out installing) | Hadoop Eco components are being installed on the created VMs. |
Running(Scale out starting) | Components are being executed. |
Running(Scale out running) | Checking the operation of the existing cluster and expanded VMs. |
Running(Scale in Initializing) | Received a cluster reduction request and checking if the target VMs can be deleted. |
Running(Scale in ready) | Terminating components on VMs targeted for reduction. |
Running(Scale in starting) | Inspecting whether component termination on target VMs was successful. |
Running(Scale in terminating) | VMs are being deleted. |
Failed to scale out | Failed to create VMs for expansion. |
Failed to scale out vm | Failed to install or execute components on expansion target VMs. |
Failed to scale in | Failed during the deletion of target VMs for reduction. |
Failed to scale in vm | Failed to normally terminate components on target VMs for reduction. |
Terminating | The cluster is being terminated. |
Terminated(User) | The cluster was terminated by the user. |
Terminated(UserCommand) | The cluster was terminated because task scheduling finished normally. |
Terminated(Scale in) | The cluster was reduced, and VMs were terminated normally. |
Terminated(Error) | The cluster was terminated due to an error. |
Terminated(Failed to create vm) | An error occurred during VM creation. |
Terminated(Failed to destroy vm) | An error occurred during VM termination. |
Terminated(Check time over) | Cluster creation time exceeded during component execution. |
Terminated(Install error) | Failed to install or execute components during cluster creation, leading to termination. |
Terminated(Failed to scale out) | VMs were terminated due to cluster expansion failure. |
Terminated(Failed to scale in) | VMs were forcibly terminated after failing to terminate components normally. |
Terminated(User deleted VM) | The user arbitrarily deleted a Hadoop Eco cluster VM. |
Pending | Hadoop Eco creation can be requested after Open API activation. |
Processing | Hadoop Eco creation and job scheduling are in progress after Open API activation. |
Instance and cluster states
Instances are KakaoCloud Virtual Machines that constitute the cluster; the status of an instance and the cluster may differ.
Cases where statuses differ include:
- If a Master node instance is not in the
Activestate and the availability type isSingle, the cluster will not operate normally. - If the availability type is
HA, the cluster can operate normally as long as one of the instances for Master node 1 or 2 is in theActivestate.
Components
The list of components running on a Hadoop Eco cluster is as follows:
Core Hadoop
- Standard (Single)
- HA (High Availability)
| Location | Component | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Master 1 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:50070 HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8088 | |
| TimelineServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8188 | |
| JobHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:19888 | |
| SparkHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:18082 | |
| SparkThriftServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:20000 | |
| TezUI | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9999 | |
| HiveServer2 (HS2) | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:10002 | |
| Hue | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8888 | |
| Zeppelin | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8180 | |
| Oozie | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:11000 |
| Location | Component | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Master 1 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:50070HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8088 | |
| HiveServer2 (HS2) | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:10002 | |
| Master 2 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:50070HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:8088 | |
| HiveServer2 (HS2) | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:10002 | |
| Master 3 | TimelineServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8188 |
| JobHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:19888 | |
| SparkHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:18082 | |
| SparkThriftServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:20000 | |
| TezUI | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:9999 | |
| HiveServer2 (HS2) | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:10002 | |
| Hue | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8888 | |
| Zeppelin | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8180 | |
| Oozie | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:11000 |
HBase
- Standard (Single)
- HA (High Availability)
| Location | Component | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Master 1 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:50070 HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8088 | |
| HMaster | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:16010 | |
| TimelineServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8188 | |
| JobHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:19888 | |
| Hue | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8888 |
| Location | Component | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Master 1 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:50070 HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8088 | |
| HMaster | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:16010 | |
| Master 2 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:50070 HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:8088 | |
| HMaster | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:16010 | |
| Master 3 | HMaster | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:16010 |
| TimelineServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8188 | |
| JobHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:19888 | |
| Hue | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8888 |
Trino
- Standard (Single)
- HA (High Availability)
| Location | Component | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Master 1 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:50070HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8088 | |
| Trino Coordinator | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8780 | |
| TimelineServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8188 | |
| JobHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:19888 | |
| TezUI | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9999 | |
| HiveServer2 (HS2) | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:10002 | |
| Hue | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8888 | |
| Zeppelin | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8180 |
| Location | Component | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Master 1 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:50070 HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8088 | |
| HiveServer2 (HS2) | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:10002 | |
| Master 2 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:50070 HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:8088 | |
| HiveServer2 (HS2) | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:10002 | |
| Master 3 | Trino Coordinator | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8780 |
| TimelineServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8188 | |
| JobHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:19888 | |
| TezUI | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:9999 | |
| HiveServer2 (HS2) | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:10002 | |
| Hue | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8888 | |
| Zeppelin | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8180 |
Dataflow
- Standard (Single)
- HA (High Availability)
| Location | Component | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Master 1 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:50070 HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8088 | |
| TimelineServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8188 | |
| JobHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:19888 | |
| Kafka Broker | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9092 | |
| Druid Master | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:3001 | |
| Druid Broker | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:3002 | |
| Druid Router | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:3008 | |
| Superset | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:4000 | |
| Hue | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8888 |
| Location | Component | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Master 1 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:50070HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:8088 | |
| Kafka Broker | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:9092 | |
| Druid Master | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:3001 | |
| Druid Broker | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-1}:3002 | |
| Master 2 | HDFS NameNode | Below HDE-2.0.0: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:50070HDE-2.0.0 or higher: http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:9870 |
| YARN ResourceManager | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:8088 | |
| Kafka Broker | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:9092 | |
| Druid Master | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:3001 | |
| Druid Broker | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-2}:3002 | |
| Master 3 | TimelineServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8188 |
| JobHistoryServer | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:19888 | |
| Kafka Broker | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:9092 | |
| Druid Master | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:3001 | |
| Druid Broker | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:3002 | |
| Druid Router | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:3008 | |
| Superset | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:4000 | |
| Hue | http://{HadoopMST-cluster-3}:8888 |
Instance
Instances can be viewed in the Cluster List and can be handled identically to general VM operations.
For stable operation, it is recommended that Master node instances have at least 16GB of memory and Worker node instances have at least 32GB.
Volume
A volume is the basic storage where an image is configured when creating an instance, representing HDFS capacity. To ensure stable HDFS operation, an appropriate size must be selected. For more details on volumes, please refer to the Create and Manage Volumes guide.
Network and Security
All instances created in Hadoop Eco are provided in a VPC environment. To configure a cluster, security groups must be created and inbound rules for component configuration must be set. For more details on network and security settings, please refer to the Security Groups guide.