Video Transcoding
Video transcoding instances are designed to provide real-time video transcoding. These instances are highly suitable for live event broadcasts, video conferencing, and real-time transcoding applications.
These instances are provided by the Virtual Machine.
- Applicable type:
vt1a
vt1a
vt1a instances are powered by 3rd generation AMD EPYC 7003 series processors and are suitable for live video transcoding workloads.
Hardware specifications
- Up to 3.6Ghz 3rd generation AMD EPYC processor (AMD EPYC 7643)
- Up to 50Gbps network bandwidth
- Support for up to 8 Xilinx U30 media accelerator FPGA cards including accelerated H.264/AVC and H.265/HEVC codecs
- Support for resolutions up to 4K UHD
- Support for AMD instruction sets (AVX, AVX2)
Use cases
Live event broadcasting, video conferencing, and real-time transcoding
Details
| Instance size | FPGA | vCPU | Memory (GiB) | Network bandwidth (Gbps) | 1080p60 Streams | 4Kp60 Streams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
vt1a.4xlarge | 1 | 16 | 48 | Max 6 | 8 | 2 |
vt1a.8xlarge | 2 | 32 | 96 | Max 25 | 16 | 4 |
vt1a.32xlarge | 8 | 128 | 384 | Max 50 | 64 | 16 |
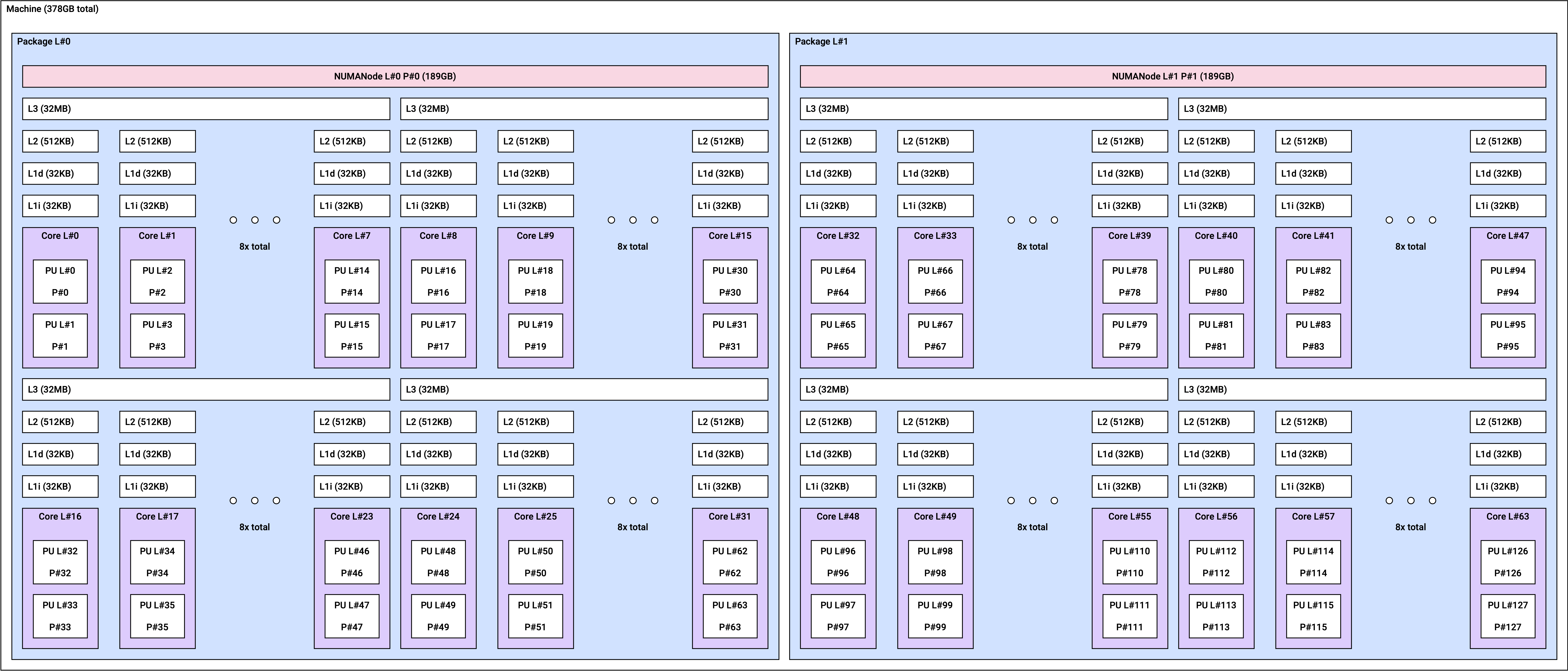
NUMA topology
In Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) architecture, each CPU can access its own allocated memory (local memory). Using NUMA architecture allows for sharing memory across multiple processors, thus achieving high scalability.
vt1a instances have the following NUMA topology according to the instance size.
| Instance size | Number of NUMA domains | Cores per NUMA domain |
|---|---|---|
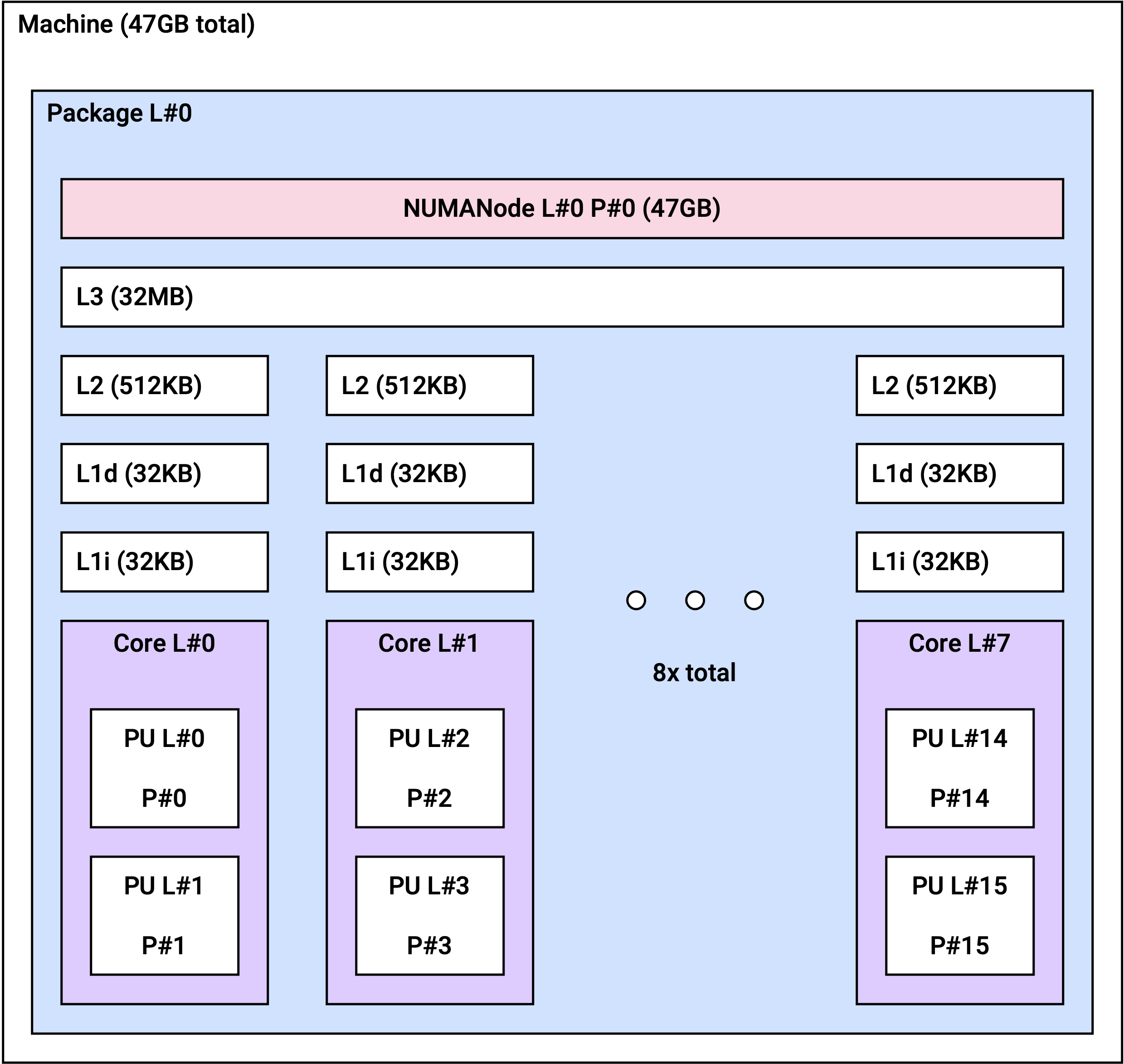
vt1a.4xlarge | 1 | 8 |
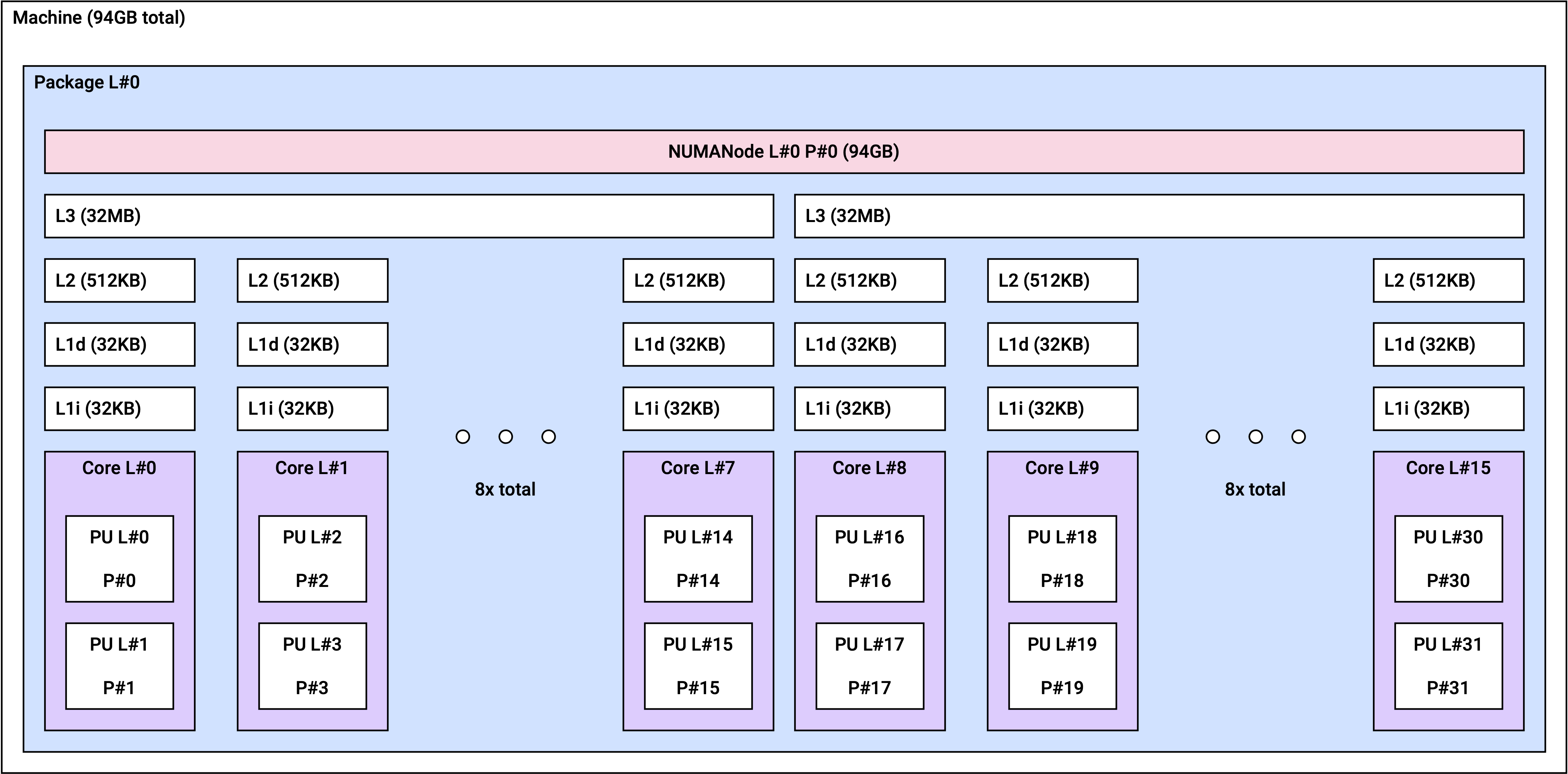
vt1a.8xlarge | 1 | 16 |
vt1a.32xlarge | 2 | 32 |
NUMA topology architecture
vt1a.4xlarge
vt1a.8xlarge
vt1a.32xlarge