Create and manage image
An image is a template that includes an operating system, applications, and configuration settings required to run a virtual machine.
Depending on your use case, you can start an instance using an image that includes the necessary OS and applications.
View image list
You can view the list of images currently in use and check information for each image.
-
Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
-
In the Image menu, check the list of currently used images.
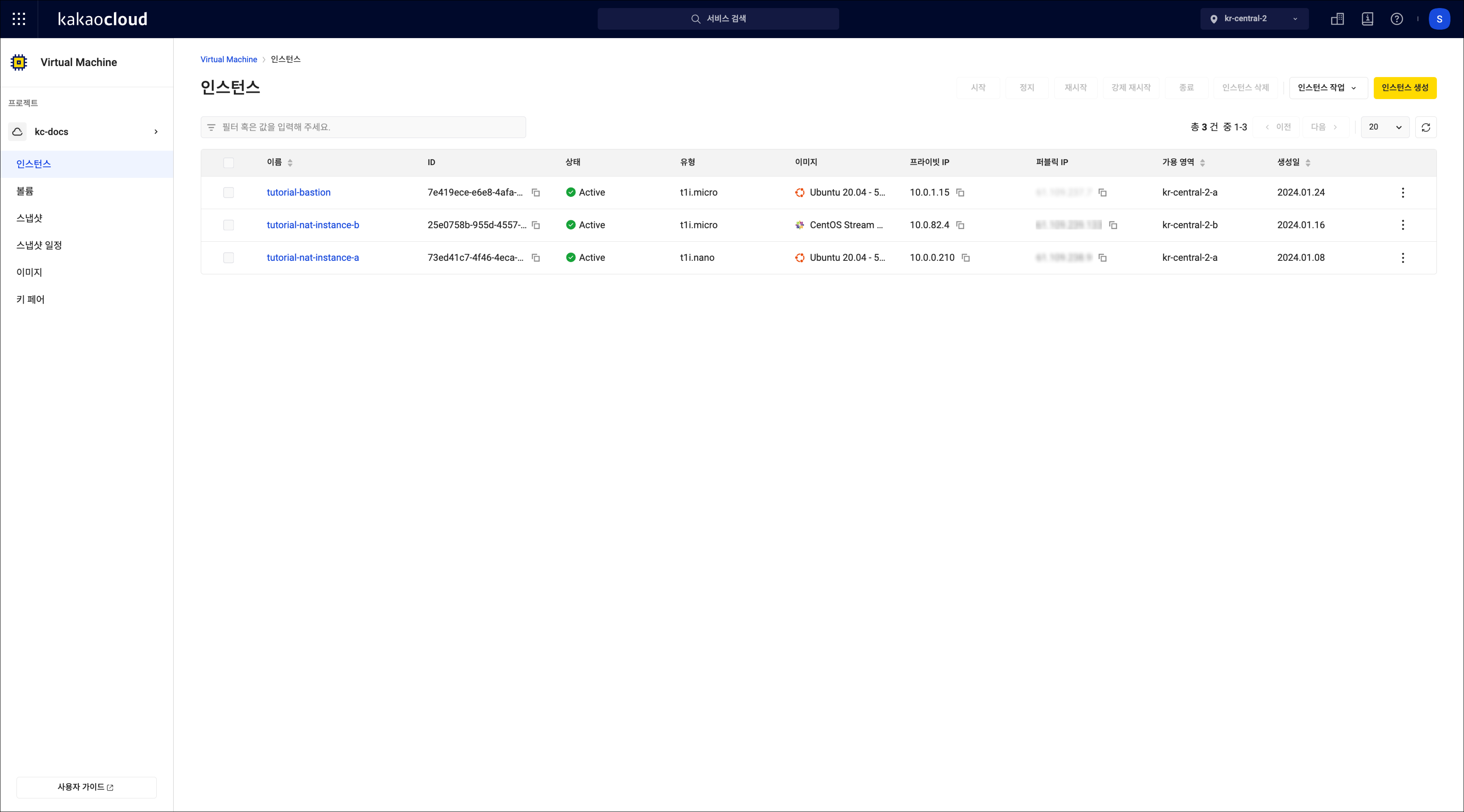 View image list
View image listType Description Default Images officially provided by KakaoCloud My images Images created by the user
- You can edit or delete the image name and description
Windows-based images provided as default images do not apply to free credits. Please take note when using them.
Create my image
You can create an image from the current state of an instance. Created images can later be used to launch new instances.
Only the root volume with an operating system installed can be used to create an image. To back up additional volumes, use the snapshot feature.
-
Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
-
In the Instance menu, select the [More] icon for the desired instance and select Create image.
-
In the Create image popup, enter the required information and select [Create].
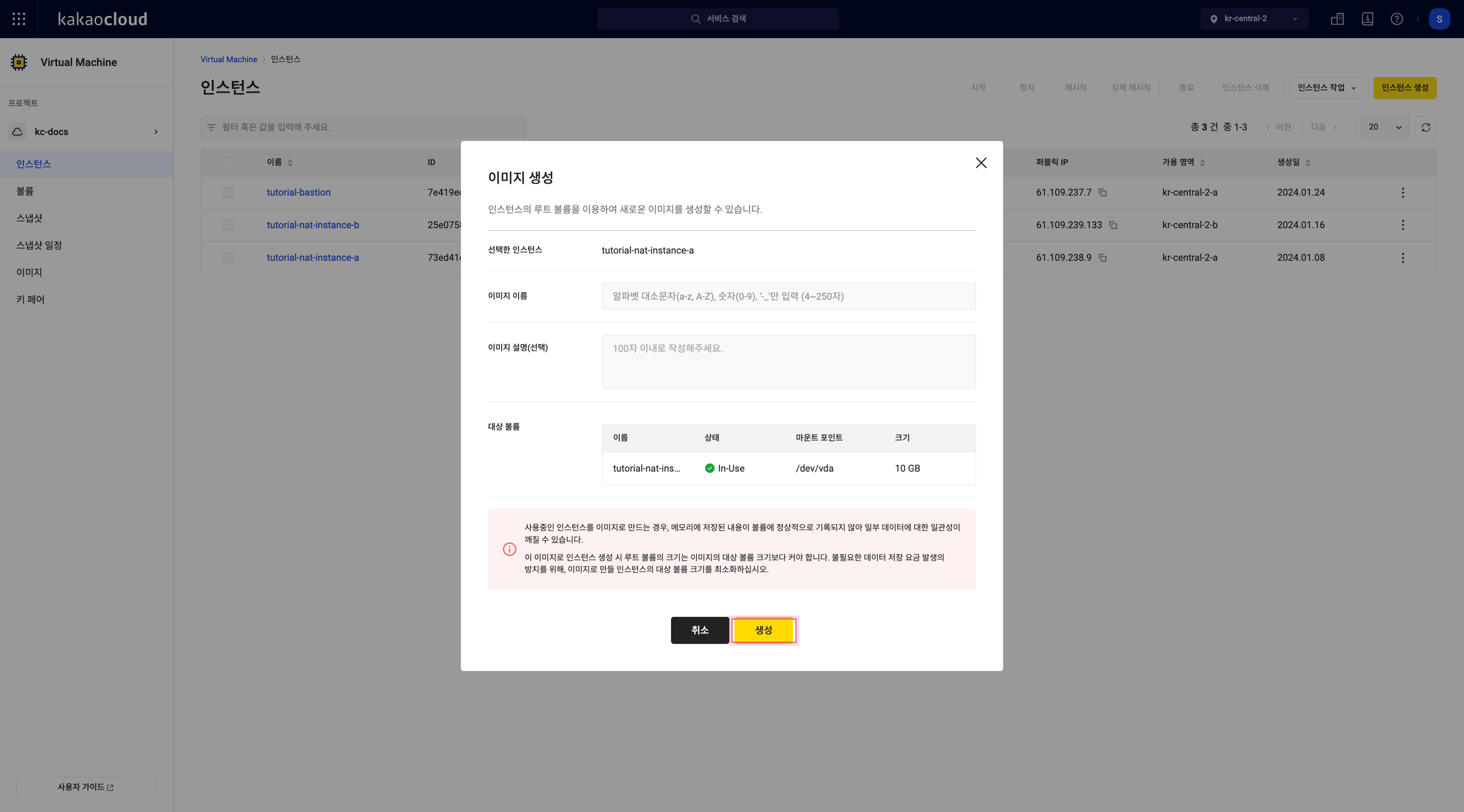 Create image
Create image
Create instance with my image
You can create an instance using information stored in a custom image.
-
Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
-
In the Image menu, select the My images tab.
-
Select Create instance for the desired image.
- The selected image will be prefilled in the Create instance screen.
- You can switch to a different image under the My images tab.
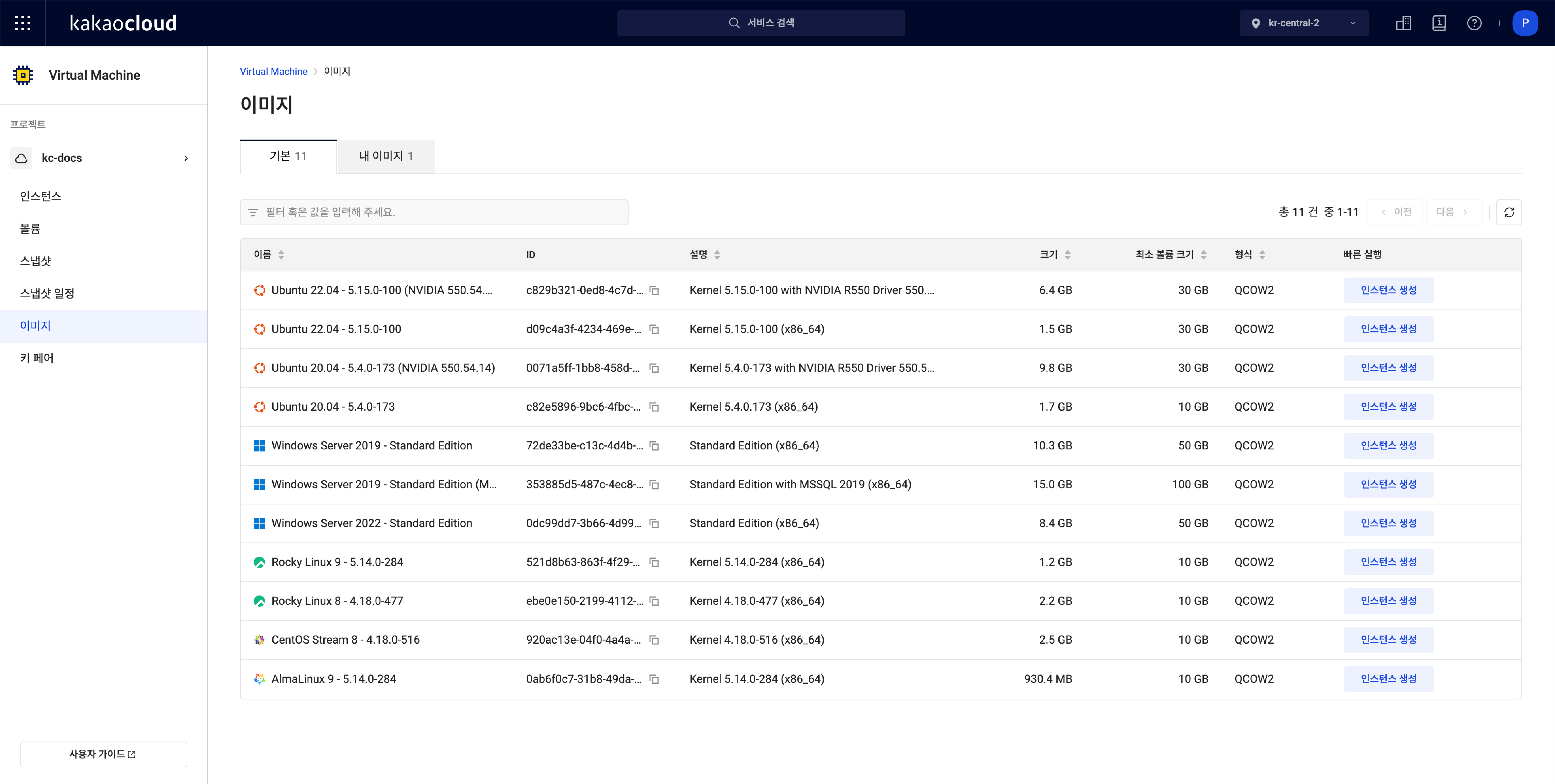
-
Enter the necessary information and select [Create].
Modify my image
You can update information for your custom image.
If the image was shared from another project, only the creator can modify it.
- Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
- In the Image menu, select the My images tab.
- Select the [More] icon for the image to update and select Edit image.
- In the Edit image popup, edit the information and select [Save].
Share my image
You can share custom images with other projects within your account.
- Only the creator of an image can share or unshare it.
- Members of projects that received the shared image will see a [Shared] icon next to the image.
-
Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
-
In the Image menu, select the My images tab.
-
Select the [More] icon for the image to share and select Share image.
-
In the Share image popup, select the target project and select [Share].
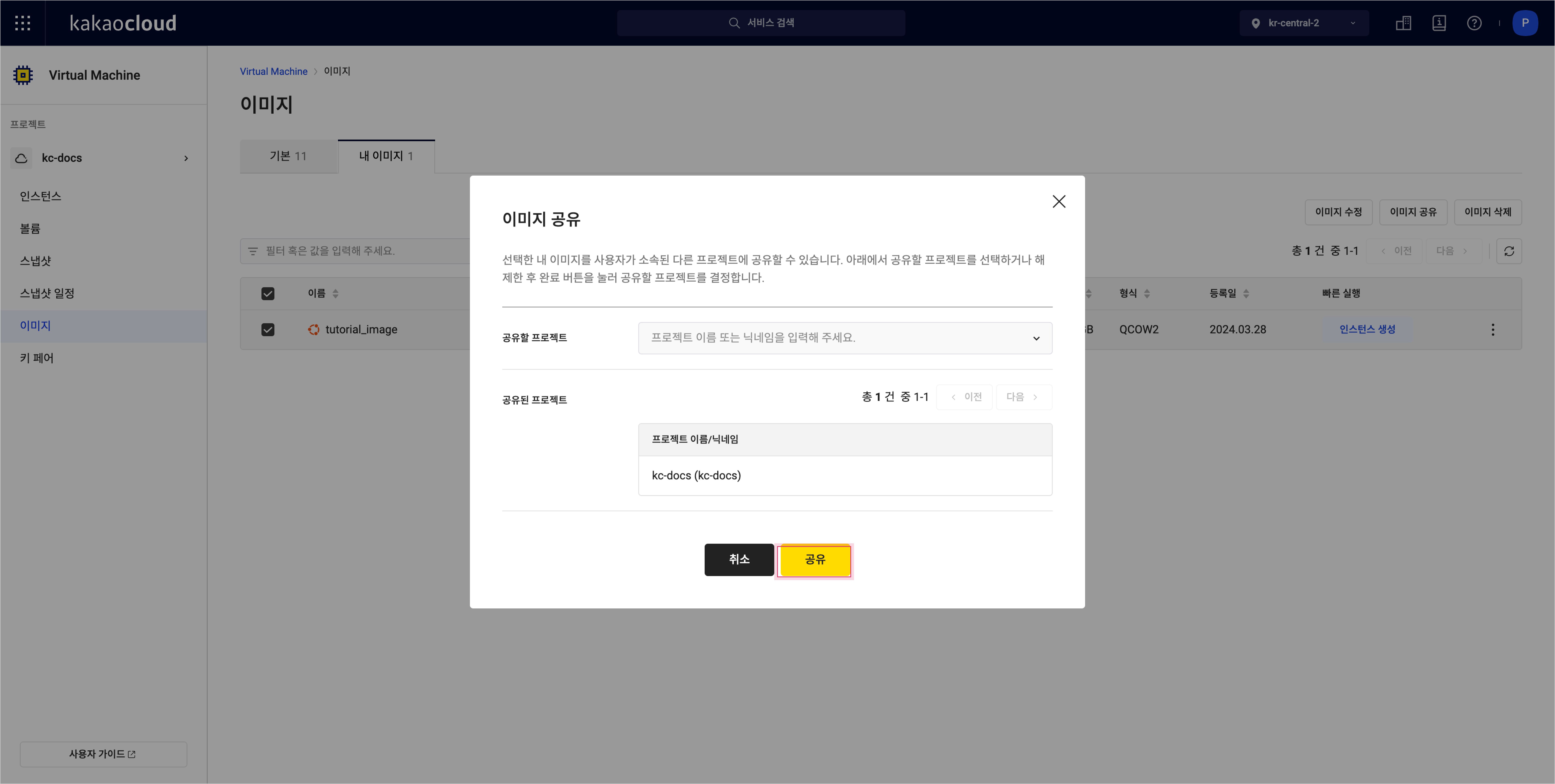 Share image
Share image
Delete my image
You can delete images that are no longer needed.
- You can only delete images you created.
- If the image was shared from another project, only the creator can delete it.
- Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
- In the Image menu, select the My images tab.
- Select the [More] icon for the image to delete and select Delete image.
- In the Delete image popup, enter the image name and select [Delete].
Change root volume partition table format
Some OS-based instances use the MBR (Master Boot Record) partition table scheme for the root volume by default. MBR supports up to 4 partitions and disks up to 2.0 TB. GPT (GUID Partition Table), on the other hand, has no such limitations.
KakaoCloud provides cloud images without modification to OS-level settings. Instances based on CentOS, CentOS Stream, or Rocky Linux may use MBR for the root volume, but you can convert them to GPT.
The partition table format and file system type for each OS image are as follows:
| OS name | Version | Root volume partition table |
|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu | 20.04 | GPT |
| Ubuntu | 22.04 | GPT |
| Ubuntu | 24.04 | GPT |
| CentOS Stream | 9 | MBR |
| Rocky Linux | 8.10 | MBR |
| Rocky Linux | 9.4 | MBR |
| Alma Linux | 8.10 | GPT |
| Alma Linux | 9.4 | GPT |
| Windows | 2019 | MBR |
| Windows | 2022 | MBR |
Procedure
Here's how to convert the disk partition table format from MBR to GPT for a CentOS instance.
This example uses the CentOS Stream 8 image provided by KakaoCloud.
Changing the partition table of a disk in use may cause data loss. Always back up before proceeding.
-
Check current disk info with
lsblk:Klsblk 명령[root@centos ~]$ sudo fdisk -l
Disk /dev/vda: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes, 20971520 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0009b542
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/vda1 * 2048 20971486 10484719+ 83 Linux -
Check the current partition table using
gdisk:gdisk 명령[root@centos ~]$ sudo gdisk -l /dev/vda
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10
Partition table scan:
MBR: MBR only
BSD: not present
APM: not present
GPT: not present
***************************************************************
Found invalid GPT and valid MBR; converting MBR to GPT format
in memory.
***************************************************************
Disk /dev/vda: 20971520 sectors, 10.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): 79C4C601-BF62-45E4-97F8-AB21F158EED7
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 20971486
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 2014 sectors (1007.0 KiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 20971486 10.0 GiB 8300 Linux filesystem -
Use
gdiskto convert the disk from MBR to GPT.- GPT requires a boot partition.
- Create a boot partition from sector 34 to 2047 with code
ef02.
-
Install GRUB on the new boot partition:
Install GRUB[root@centos ~]$ sudo partprobe
[root@centos ~]$ sudo grub2-install /dev/vda
Installing for i386-pc platform.
Installation finished. No error reported. -
Reboot to apply changes:
Reboot command[root@centos ~]$ sudo reboot -
Confirm the change using
fdisk -l:Check conversion[root@centos ~]$ sudo fdisk -l
WARNING: fdisk GPT support is currently new, and therefore in an experimental phase. Use at your own discretion.
Disk /dev/vda: 3221.2 GB, 3221225472000 bytes, 6291456000 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: gpt
Disk identifier: D9C42684-E18C-4B8F-9388-C2F2CDC093ED
# Start End Size Type Name
1 2048 6291455965 3T Linux filesyste Linux filesystem
2 34 2047 1007K BIOS boot BIOS boot partition