Manage instance
This section explains how to manage instances in the Virtual Machine service.
View instance list
You can view, search, and manage running instances and their details.
-
Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
-
In the Instance menu, view the list of running instances. Use filters to sort instances by various properties.
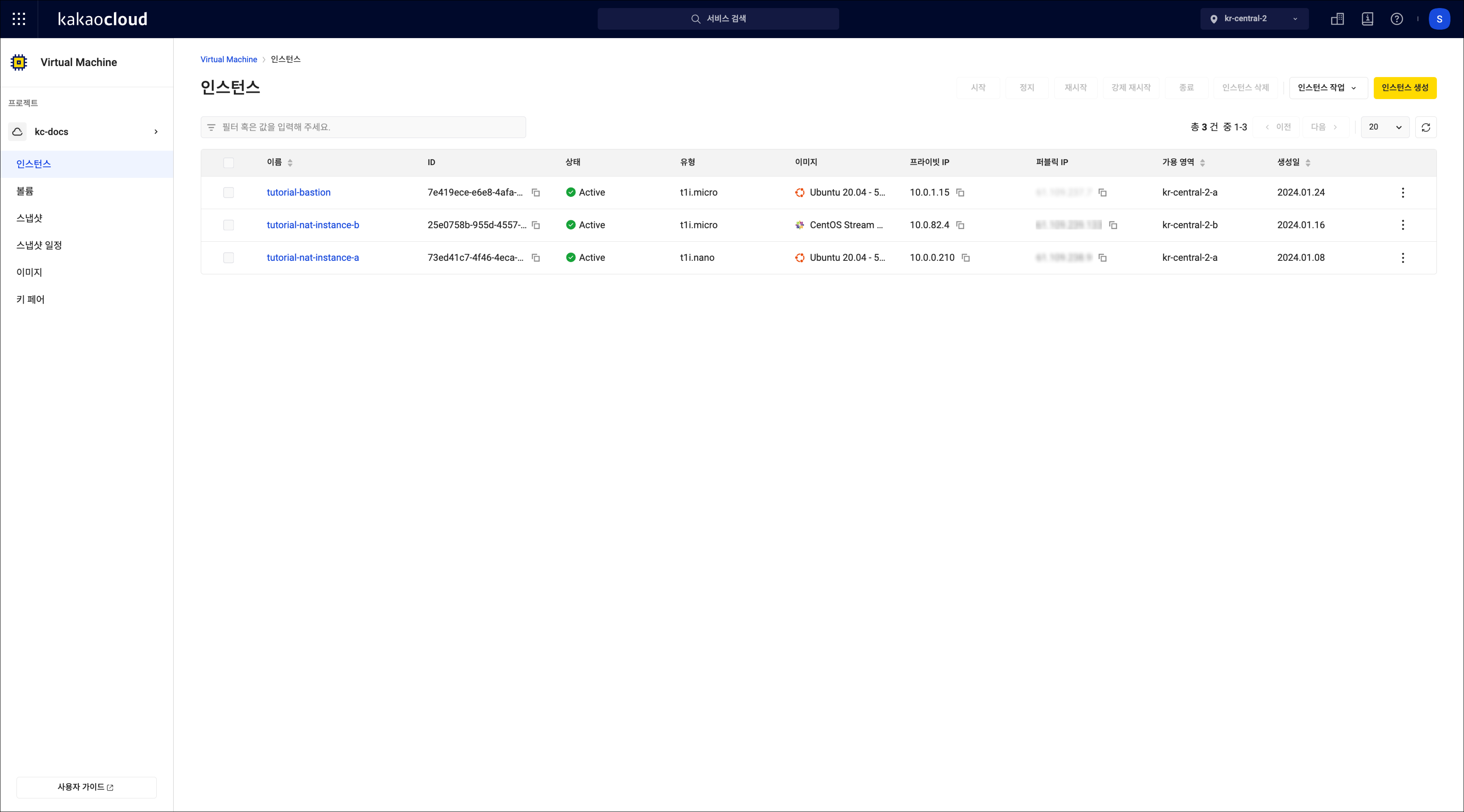
Field Description Name User-defined instance name ID Unique ID of the instance Status Current state of the instance
- See Instance state and billingType Instance server type
- Hover to view details (vCPU, memory)Image Installed image on the instance Default private IP Private IP assigned to the instance's default network interface Default public IP Public IP associated with the instance's default network interface Availability zone The availability zone where the instance resides Creation time Instance creation date More Execute functions by clicking [More]
- See More features
More features
Select the [More] icon next to an instance to access additional features.
-
Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
-
In the Instance menu, select the [More] icon beside the desired instance and select an action.
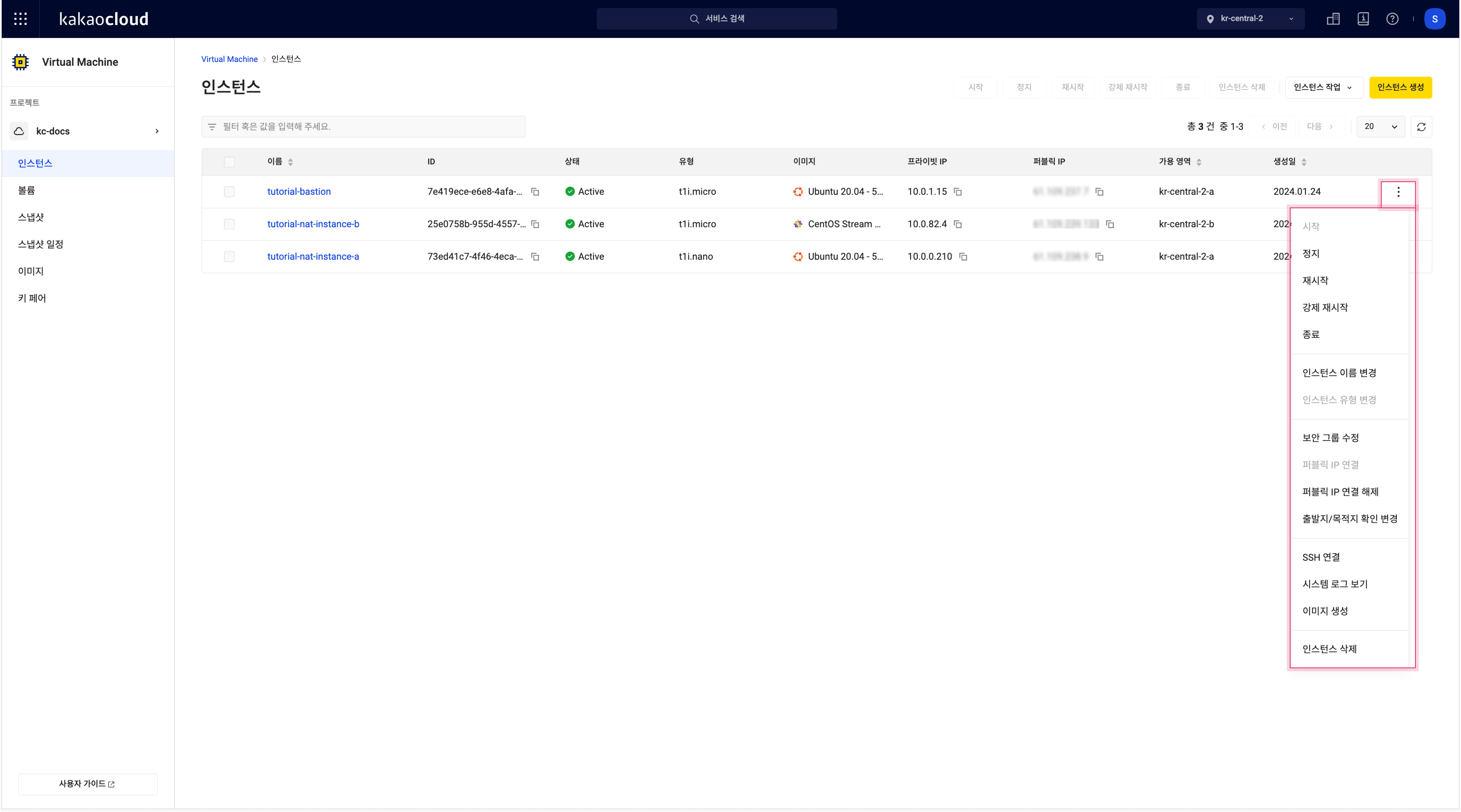 Instance more menu
Instance more menuFeature Description Resulting status Start Start an instance from StoppedorShelvedstateActiveStop Stop a running instance StoppedRestart Soft reboot ActiveForce restart Hard reboot ActiveTerminate Shelve the instance Shelved_offloadedDelete instance Permanently delete and release the instance - Rename instance Rename or update the description - Resize instance Change instance type
- Available only inStoppedstate- Attach network interface Add a secondary network interface - Detach network interface Remove a secondary network interface - Modify security group Update security group settings - Associate public IP Assign public IP
- Admin only- Disassociate public IP Remove public IP
- Admin only- Modify allowed source IPs Add or remove allowed outbound source IPs or CIDRs
- Up to 10 entries- SSH connect Show SSH connection instructions
- For Linux instances only- RDP connect Show RDP connection instructions
- For Windows instances only- View system log View system log popup (Linux only) - Create image Create image from root volume
💡 Although you can create images in bothActiveandStoppedstates, it is recommended to useStoppedto ensure data integrity.-
- When you modify the allowed source IPs, the interface accepts packets only from the specified IP addresses or CIDRs.
View instance details
You can view detailed info about the instance, including networking, security, volumes, activity logs, and monitoring.
- Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
- In the Instance menu, select the desired instance.
- Use the tabs to view the corresponding information.
- Details
- Network
- Security
- Volumes
- Activity log
- Monitoring
View general information about the instance.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Instance name | User-defined name |
| Instance ID | Unique UUID |
| Instance status | Current state |
| Availability zone | Location of the instance |
| Hostname | Auto-assigned hostname based on private IP (e.g., host-10-0-0-1) |
| Instance type | Type selected at creation |
| Image | Image used for creation |
| vCPU | Number of virtual CPUs |
| Key pair | Assigned SSH key pair |
| Memory | Memory size |
| CPU multithreading | Whether multithreading is enabled |
| Volumes | Number of attached volumes |
| Created by | User who created the instance |
| Volume size | Total disk size |
| Created at | Creation timestamp |
View network interfaces and related details.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface name | Name of the interface |
| Interface ID | UUID of the interface |
| Connection status | In Use or Available |
| Private IP | Assigned private IP |
| Public IP | Associated public IP (if any) |
| Availability zone | Availability zone of the interface |
| VPC name | VPC name |
| VPC ID | UUID of the VPC |
| Subnet name | Subnet name |
| Subnet ID | UUID of the subnet |
| Allowed source IPs | List of allowed CIDRs or IPs |
| More | - Modify allowed source IPs - Detach interface from instance |
View applied security groups and rules. See Modify security group.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Security groups | Applied security groups |
| Rules | Inbound and outbound rules |
View volume information.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Volume name | Name of the volume |
| Volume ID | UUID of the volume |
| Status | Current volume status - See Volume states |
| Mount point | Mount location |
| Type | Volume type |
| Size | Size in GB |
| Snapshot schedule | Associated snapshot policy |
| Delete with instance | Whether volume is deleted with the instance |
| Created at | Volume creation timestamp |
| More | - Modify volume - Attach/detach volume - Enable delete on termination - Create snapshot - Delete volume |
Track instance operations and user actions.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Request ID | - | Unique log ID |
| Action type | Create | Create instance |
| Delete | Delete instance | |
| Stop | Stop instance | |
| Shelve | Terminate instance | |
| Start | Start instance | |
| Reboot | Reboot instance | |
| Revert resize | Cancel resize | |
| Confirm resize | Confirm resize | |
| Resize | Resize instance | |
| Attach interface | Add NIC | |
| Detach interface | Remove NIC | |
| Attach volume | Add volume | |
| Detach volume | Remove volume | |
| Create image | Create image from instance | |
| User | - | ID of the user |
| Timestamp | - | Action timestamp |
Use monitoring to manage resource usage efficiently.
There are two modes: Basic monitoring and Detailed monitoring.
Delete instance
You can delete instances that are no longer needed.
Deleted instances are permanently removed and cannot be recovered.
- Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
- In the Instance menu, select the [More] icon > Delete instance.
- In the Delete instance popup, enter the instance name and select [Delete].
- When you delete an instance, connected network interfaces are handled as follows:
- Interfaces created as
new interfacesare deleted together with the instance. - Interfaces selected as
existing interfacesremain after deletion and must be removed manually.
- Interfaces created as
Monitoring
Monitoring is divided into basic and detailed monitoring. Detailed monitoring requires prior installation of a monitoring agent.
Basic monitoring
You can view the default monitoring data:
-
Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
-
Select the instance you want to monitor.
-
On the instance detail page, go to the Monitoring tab > Basic monitoring sub-tab.
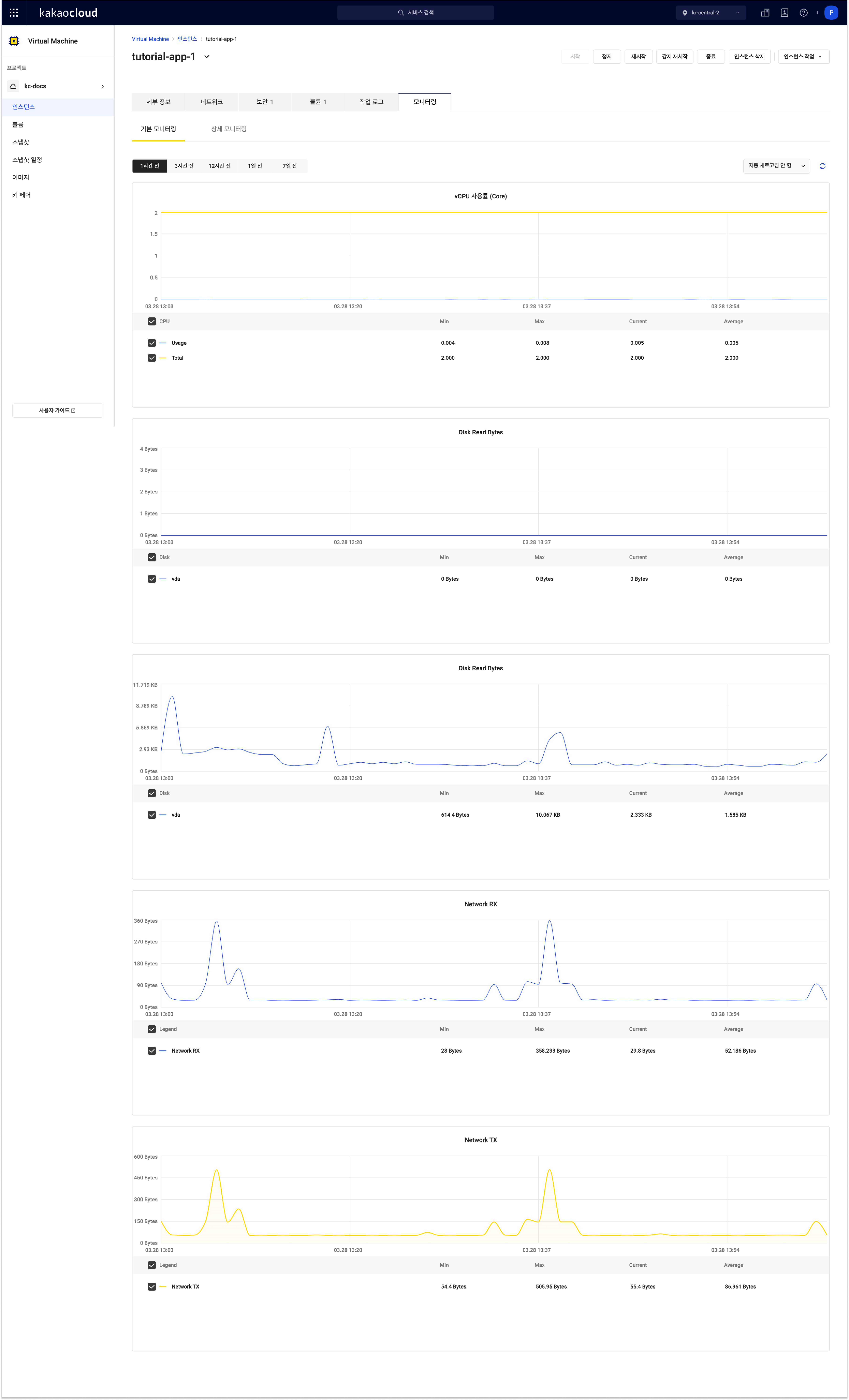 Basic monitoring
Basic monitoringMetric Description vCPU usage (Core) Total vCPU usage over time Disk Read/Write Bytes Disk (volume) I/O activity over time Network RX Network receive volume over time Network TX Network transmit volume over time Credit Usage CPU credits consumed during the measurement period (burstable instance only) Credit Balance Remaining CPU credits (burstable instance only) infoFor instances connected to multiple network interfaces, the Network RX/TX values for each network interface are displayed.
Detailed monitoring
Detailed monitoring requires the installation of a monitoring agent.
- Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
- Select the instance.
- On the detail page, select [Installation guide] in the Monitoring tab.
- Follow the guide to install the agent and configure metrics in Management > Monitoring > Explorer tab. See How to use the Explorer.
- To view logs, use the Log Explorer tab. See Log Explorer guide.
- You can customize the monitoring dashboard as needed. See Use dashboard.
Associate public IP
You can associate a public IP with an instance.
Only users with Project Admin role can perform this operation.
- Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
- In the Instance menu, select the [More] icon > Associate public IP.
- In the popup, select the network interface and private IP to associate, then select [OK].
Disassociate public IP
You can remove a public IP from an instance.
Only users with Project Admin role can perform this operation.
If the IP is only disassociated (not deleted), charges may still apply.
- Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
- In the Instance menu, select the [More] icon > Disassociate public IP.
- In the popup, select the public IP and interface, then check the box to delete the IP.
- Select [Disassociate].
Modify security group
You can change the security group attached to the instance's network interface.
-
Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
-
In the Instance menu, select the [More] icon > Modify security group.
-
In the popup, select the security group(s) to apply.
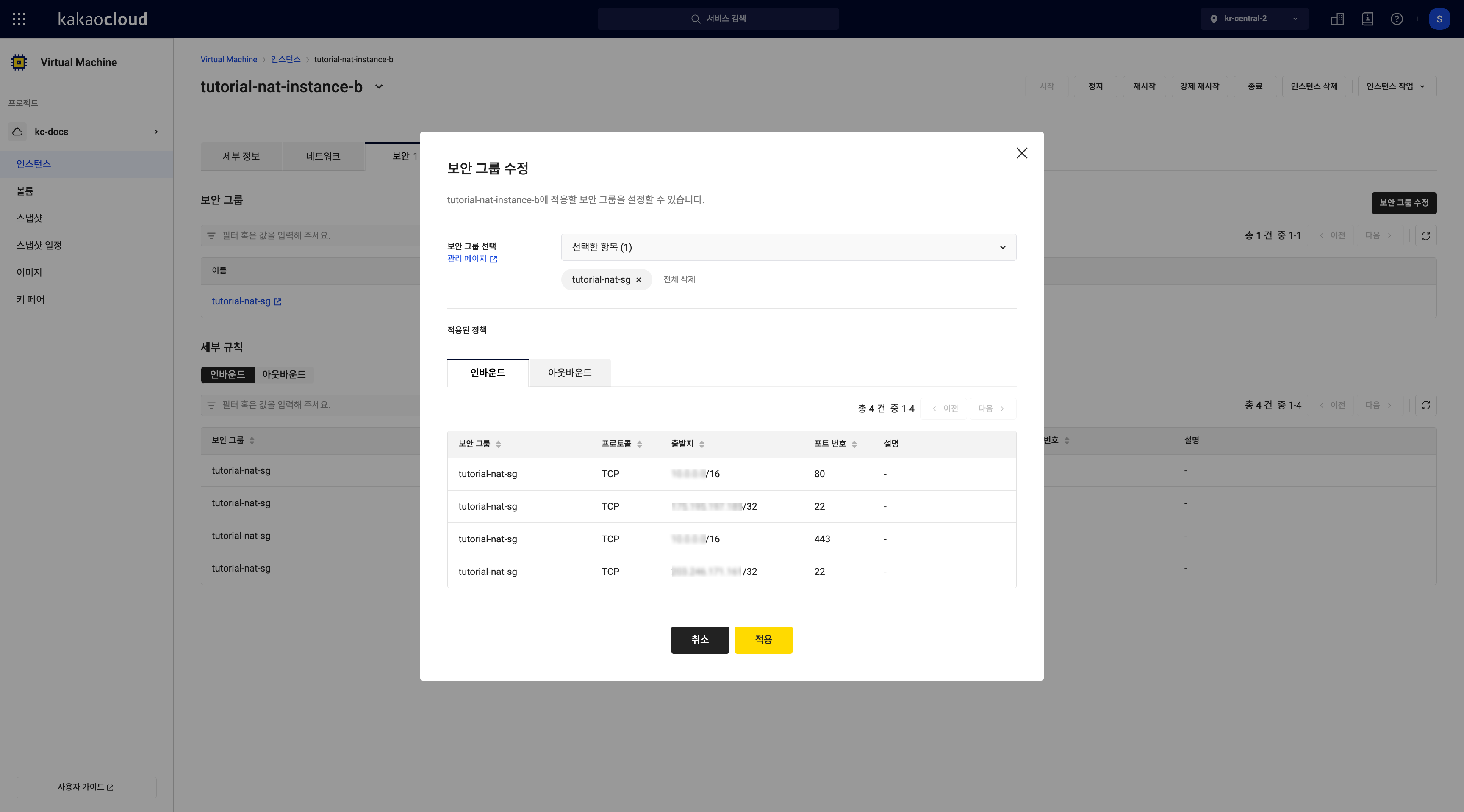 Modify security group
Modify security group -
Select [Save].
Network interface
Attach network interface
You can attach a secondary network interface to an instance.
- Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
- In the Instance menu, select the [More] icon > Attach network interface.
- In the popup, review and select the interface to attach.
- Select [OK].
Detach network interface
You can detach a secondary network interface from an instance.
Primary interfaces cannot be detached.
- Go to the KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine menu.
- In the Instance menu, select the [More] icon > Detach network interface.
- In the popup, select the interface to detach.
- Select [OK].
Set time reference
For many server operations and processes, consistent and accurate time reference is critical. KakaoCloud-provided images use default OS-based time synchronization tools such as Network Time Protocol (NTP), Chrony, and systemd-timesyncd. These tools help multiple servers operate on a unified time reference.
However, these services require internet access. In local network environments, KakaoCloud provides its own NTP service for internal time sync. For Linux-based OSes, you can configure time sync using the Chrony client.
- KakaoCloud’s internal NTP service is available at IPv4 address
169.254.169.123.
- RHEL-based
- Debian-based
-
Install the Chrony package:
sudo yum install chrony -
Edit
/etc/chrony.confand add the following line:server 169.254.169.123 prefer iburst minpoll 4 maxpoll 4 -
Restart the chronyd daemon:
sudo service chronyd restart -
Enable chronyd on boot:
sudo chkconfig chronyd on -
Verify that Chrony is using the KakaoCloud NTP IP and check if
^*is set:chronyc sourcesOutputMS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^- 193.123.243.2 2 6 17 9 -8932us[-8909us] +/- 4550us
^- ec2-13-209-84-50.ap-nort> 2 6 17 9 -8534us[-8512us] +/- 5038us
^* 169.254.169.123 2 4 17 9 +11us[ +34us] +/- 39ms -
Check Chrony tracking status:
chronyc trackingOutputReference ID : A9FEA97B (169.254.169.123)
Stratum : 3
Ref time (UTC) : Wed Jun 28 08:14:40 2023
System time : 0.000019450 seconds fast of NTP time
Last offset : +0.000022669 seconds
RMS offset : 0.000022669 seconds
Frequency : 1.352 ppm slow
Residual freq : +2.810 ppm
Skew : 0.061 ppm
Root delay : 0.076084495 seconds
Root dispersion : 0.000831026 seconds
Update interval : 2.0 seconds
Leap status : Normal
-
Install the Chrony package:
sudo apt install chrony -
Edit
/etc/chrony/chrony.confand add the following line:server 169.254.169.123 prefer iburst minpoll 4 maxpoll 4 -
Restart the chronyd daemon:
sudo /etc/init.d/chrony restart -
Verify that Chrony is using
169.254.169.123and check if it is marked as^*:Check time sync sourcechronyc sourcesOutputMS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^* 169.254.169.123 2 4 37 4 +41us[ +189us] +/- 39ms
^- pugot.canonical.com 2 6 17 18 -8895us[-8864us] +/- 162ms
^- prod-ntp-3.ntp1.ps5.cano> 2 6 17 18 -3232us[-3203us] +/- 125ms
^- prod-ntp-5.ntp1.ps5.cano> 2 6 17 19 -1723us[-1707us] +/- 123ms
^- alphyn.canonical.com 2 6 17 18 -2344us[-2321us] +/- 140ms
^- 121.174.142.82 3 6 17 19 -9870us[-9853us] +/- 28ms
^- ntp-seoul.gombadi.com 2 6 17 20 -8532us[-8519us] +/- 52ms
^- send.mx.cdnetworks.com 2 6 17 18 -8997us[-8971us] +/- 29ms
^- 193.123.243.2 2 6 17 19 -9014us[-8994us] +/- 4132us -
Check Chrony tracking status:
Check sync statuschronyc trackingOutputReference ID : A9FEA97B (169.254.169.123)
Stratum : 3
Ref time (UTC) : Wed Jun 28 08:25:52 2023
System time : 0.000156159 seconds slow of NTP time
Last offset : -0.000184961 seconds
RMS offset : 0.000184961 seconds
Frequency : 5.999 ppm fast
Residual freq : -0.600 ppm
Skew : 35.807 ppm
Root delay : 0.076914668 seconds
Root dispersion : 0.000669460 seconds
Update interval : 16.2 seconds
Leap status : Normal