Key Concepts
The key concepts of the Kubernetes Engine service are as follows.
Cluster
A cluster is the fundamental resource of Kubernetes Engine, where all Kubernetes objects, including container applications, are executed.
Clusters provided by Kubernetes Engine are configured for high availability. The control plane is deployed and managed within a VPC managed by KakaoCloud, while the worker nodes are deployed in the user’s VPC, giving users control over the node infrastructure. The cluster architecture is illustrated below:
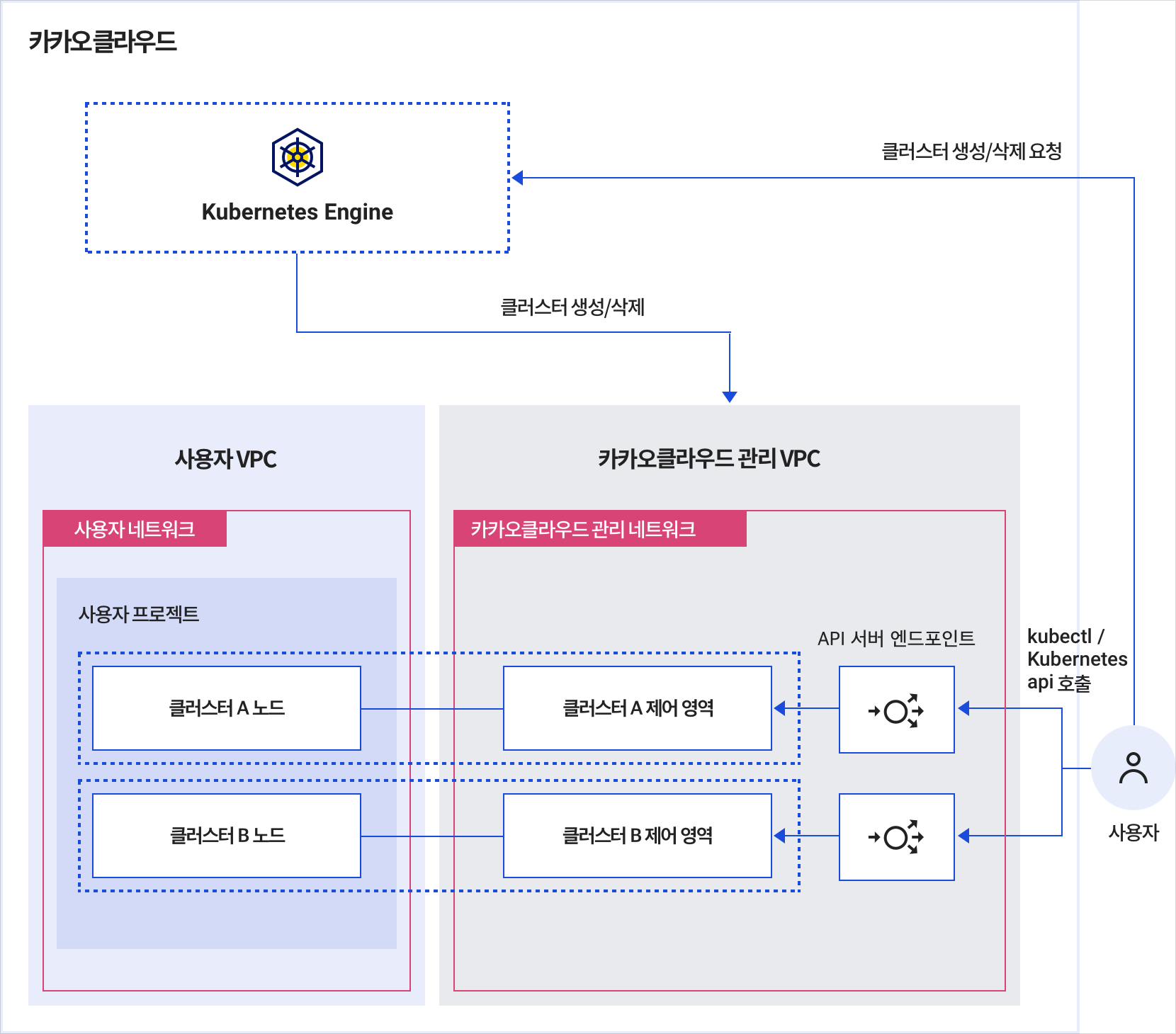 Cluster architecture
Cluster architecture
Control plane
The control plane is the master node that manages the cluster and acts as the unified entry point for the cluster.
All interactions with the cluster are made via API calls to the Kubernetes API server in the control plane. You can manage the cluster by executing commands via the HTTP/gRPC protocol, the Kubernetes CLI tool (kubectl), or the console UI. The control plane is deployed within KakaoCloud’s managed VPC and only exposes the API endpoint to users.
Node
A node, or worker node, is a server where containerized applications run.
A cluster consists of one or more nodes, which are VM instances provided by the Virtual Machine service.
When a cluster is created in Kubernetes Engine, users can create node pools. Based on the configured node pool, nodes are automatically created and deployed in specific subnets within the user's VPC.
Each node provides the necessary resources and services to run containerized applications and includes the Kubernetes node agent, kubelet, which communicates with the control plane to allow container scheduling.
Node pool
A node pool is a group of nodes with the same instance type. Kubernetes Engine manages nodes in node pool units.
The node pool created during cluster creation becomes the initial pool. Additional node pools with different instance types can later be added.
Each node in a node pool includes a Kubernetes node label kakaoi.io/kke-nodepool with the node pool's name as its value.
- The size of a node pool can be adjusted by changing the number of nodes; however, individual nodes within a node pool cannot be selectively deleted.
- When the initial node pool is created, the latest supported Kubernetes version is selected. Node pools can be managed and updated independently afterward.
CNI
Kubernetes Engine supports CNIs (Container Network Interface), which manage network configurations and communication between nodes and pods.
KakaoCloud Kubernetes Engine supports Calico and Cilium CNI plugins.
The selected CNI plugin is installed with the cluster during creation. Users can choose the CNI plugin that best fits their service environment.
The selected CNI cannot be changed after the cluster is created.
IAM role management
IAM role management in Kubernetes Engine is based on Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and integrates with IAM project roles for managing cluster resources.
Users with project-level permissions can manage all resources within the project. All resources are managed under a project hierarchy.
IAM project roles include:
- Project Admin
- Project Member
- Project Reader
| IAM permission | Project Admin ✓ | Project Member ✓ | Project Reader ✓ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manage project members | ✓ | ||
| Create cluster | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Delete cluster | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Modify cluster | ✓ | ✓ | |
| View cluster | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Add node pool | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Delete node pool | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Modify node pool | ✓ | ✓ | |
| View node pool | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Delete node | ✓ | ✓ | |
| View node | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Kubernetes RBAC
Kubernetes supports RBAC for defining fine-grained access within a cluster. Kubernetes Engine also supports this functionality.
For more details on Kubernetes RBAC, refer to the Kubernetes reference.
Resource status information
In Kubernetes Engine, the status of resources such as clusters, node pools, and nodes can be monitored. Resource status information is described below.
Cluster lifecycle and status
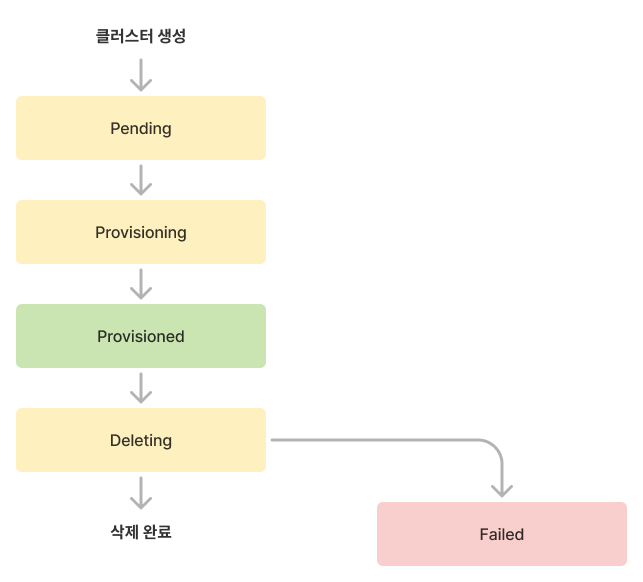 Cluster lifecycle
Cluster lifecycle
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
Provisioned | Cluster provisioning completed |
Pending | Preparing for cluster provisioning |
Provisioning | Cluster is being provisioned |
Deleting | Cluster is being deleted |
Failed | Failed state requiring user action |
Node pool lifecycle and status
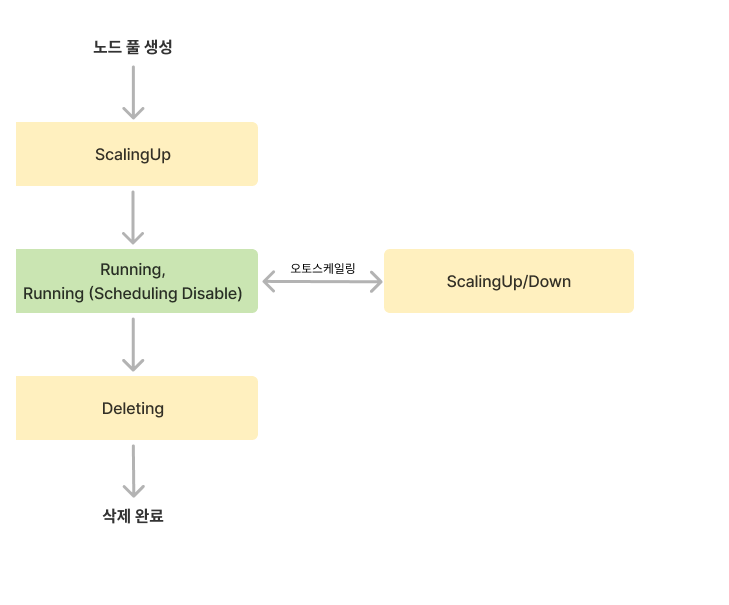 Node pool lifecycle
Node pool lifecycle
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
Running | Node pool running normally (regardless of node state) |
Running (Scheduling Disable) | All nodes in the pool have scheduling disabled |
Updating | Node pool settings are being updated |
ScalingUp | Node count is increasing |
ScalingDown | Node count is decreasing |
Deleting | Node pool is being deleted |
Failed | Failed state requiring user action |
Node lifecycle and status
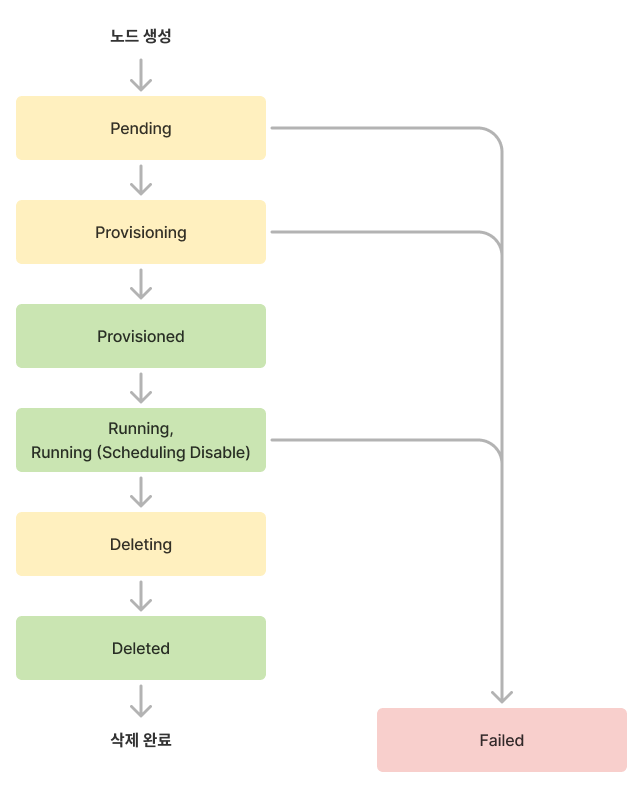 Node lifecycle
Node lifecycle
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
Running | Node is ready and running |
Running (Scheduling Disable) | Node has scheduling disabled (does not affect already scheduled pods) |
Provisioned | Node provisioning completed |
Deleted | Node has been deleted |
Pending | Preparing for node provisioning |
Provisioning | Node is being provisioned |
Deleting | Node is being deleted |
Failed | Failed state requiring user action |
Automatically generated resources during cluster/node pool creation
Certain resources are automatically generated when a cluster or node pool is created in Kubernetes Engine. These are deleted when the corresponding cluster is deleted.
| Resource type | Description |
|---|---|
| Instance | VM instance used as a node |
| Volume | Volumes used by node VMs or created via NFS client provisioner |
| Network interface | Network interface of the VM instance used as a node |
| Security group | Security group assigned to the node |
Automatically generated resources (instance, volume, network interface, security group) cannot be renamed, deleted, or modified.
If any resource settings are changed, the Kubernetes Engine service may not function properly. Exercise caution when managing related resources.
Support information
Kubernetes Engine offers new Kubernetes versions after thorough stabilization and testing.
Supported Kubernetes versions
Kubernetes Engine provides tested and stabilized Kubernetes versions.
When a new version is released, refer to the Cluster update guide to update your cluster.
| Kubernetes version | Kubernetes Engine release date | Create new cluster | Use existing cluster |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.33 | November 18, 2025 | Supported | Supported |
| 1.32 | November 18, 2025 | Supported | Supported |
| 1.31 | July 22, 2025 | Supported | Supported |
| 1.30 | May 29, 2025 | Supported | Supported |
| 1.29 | December 20, 2024 | Supported | Supported |
| 1.28 | May 28, 2024 | Supported | Supported |
| 1.27 | March 18, 2024 | Not supported | Supported |
| 1.26 | August 16, 2023 | Not supported | Supported |
| 1.25 | August 16, 2023 | Not supported | Supported |
| 1.24 | February 01, 2023 | Not supported | Supported |
| 1.23 | July 07, 2022 | Not supported | Supported |
| 1.22 | July 07, 2022 | Not supported | Supported |
Supported node images
Worker node images provided by Kubernetes Engine are Ubuntu-based and optimized per Kubernetes version.
When new images are released, refer to the Node update guide to update.
Supported instances
Instances used as nodes in Kubernetes Engine are the same as those provided by the Virtual Machine service.
For details, refer to the Instance types documentation.