Build network using NAT instances in multi-availability zones
This document introduces how to deploy NAT (Network Address Translation) instances of KakaoCloud VM in each availability zone (Multi Availability Zone).
- Estimated time required: 40 minutes
- Recommended operating systems: MacOS, Ubuntu
Before you start
In the KakaoCloud VPC environment, you can deploy NAT instances in each Availability Zone (AZ).
This configuration ensures that even if one availability zone fails, workloads in other availability zones can continue communicating externally through the NAT instance in their respective zone.
This guarantees the smooth operation of the overall cloud system and prevents potential service disruptions.
About this scenario
This document explains step-by-step how to configure NAT instances in a KakaoCloud VPC environment, allowing instances in private subnets to communicate securely with external networks through NAT.
Key topics include:
- Create and configure NAT instance: Create and configure NAT instances to support external communication.
- Set up routing tables: Configure routing tables to direct external traffic from private subnets to the NAT instance in their respective availability zone.
- Configure security groups and inbound rules: Restrict inbound requests through the NAT instance to ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS).
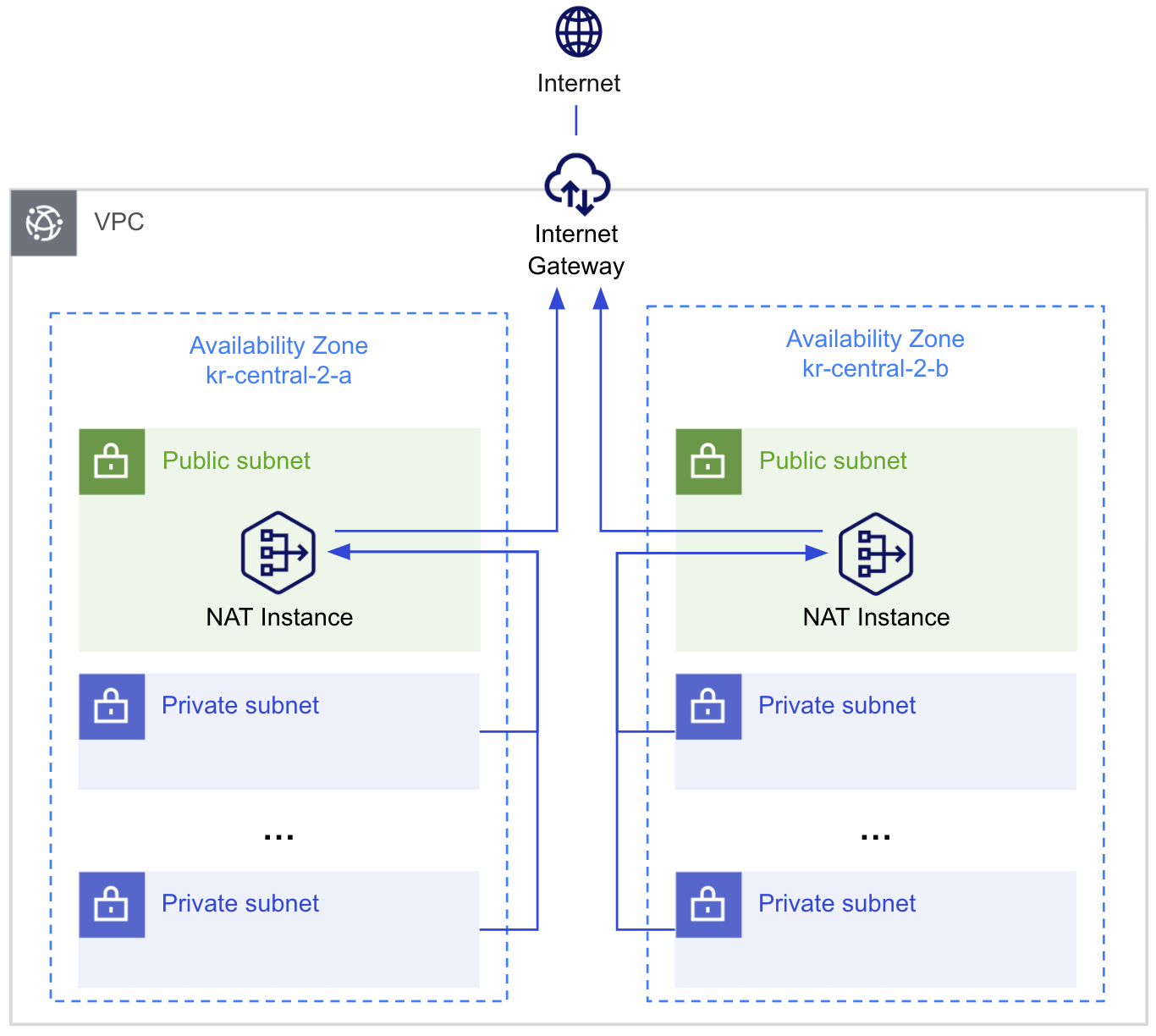
Scenario architecture
Getting started
Let's configure NAT instance that support NAT communication to connect the private subnet of KakaoCloud VPC to the internet.
Step 1. Create VPC and subnet
Create a VPC and subnets.
-
Go to KakaoCloud console > Beyond Networking Service > VPC.
-
In the VPC, select the [Create VPC] button and configure the VPC and subnets as follows:
Category Item Value VPC information VPC name tutorial VPC IP CIDR block 10.0.0.0/16 Availability Zone Number of availability zones 2 First availability zone kr-central-2-a Second availability zone kr-central-2-b Subnet configuration Number of public subnets per AZ 1 Number of private subnets per AZ 4 kr-central-2-a Public subnet IPv4 CIDR block 10.0.0.0/20 Private subnet IPv4 CIDR block 10.0.16.0/20, 10.0.32.0/20, 10.0.48.0/20, 10.0.64.0/20 kr-central-2-b Public subnet IPv4 CIDR block 10.0.80.0/20 Private subnet IPv4 CIDR block 10.0.96.0/20, 10.0.112.0/20, 10.0.128.0/20, 10.0.144.0/20 -
Verify the generated diagram and select [Create].
- The subnet status will change from
Pending Create>Pending Update>Active. Wait until it reachesActiveto proceed. - The creation process may take 5–10 minutes.
- The subnet status will change from
Step 2. Create security group for NAT instance
Enhance the security of VMs in the VPC by creating a security group and adding inbound and Outbound rules as follows:
-
Go to KakaoCloud console > Beyond Networking Service > VPC.
-
In the Security Group menu, select [Create security group].
-
Enter
tutorial-nat-sgas the Security group name. -
Select the [+ Add rule] button and set the Inbound rules as follows:
Check your public IPSelect the button below to check your current public IP address.
Description Protocol Source Port number inbound http policy TCP 10.0.0.0/16 80 inbound https policy TCP 10.0.0.0/16 443 ssh policy TCP {Your Public IP}/3222 -
Set the Outbound rules as follows:
Description Protocol Destination Port number outbound http policy TCP 0.0.0.0/0 80 outbound https policy TCP 0.0.0.0/0 443 outbound DNS policy UDP 169.254.169.253/32 (DNS Resolver endpoint for VPC) 53 outbound DNS policy 2 UDP 10.0.0.2/32 53 -
Select the [Create] button to complete the security group creation.
Step 3. Create NAT instance
NAT instances allow private subnet instances to securely communicate with external networks. NAT instances enable outbound traffic to the internet while blocking inbound traffic, enhancing security and allowing private subnet instances to receive updates and patches.
-
Go to KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine.
-
In the Instance menu, select [Create Instance] and create VM instances in two availability zones as follows:
Configuration by Availability Zone kr-central-2-a kr-central-2-b Basic information - Name: tutorial-nat-instance-a
- Count:1- Name: tutorial-nat-instance-b
- Count:1Image Ubuntu 20.04
⚠️ Select a standard image, not NVIDIA GPU typeUbuntu 20.04
⚠️ Select a standard image, not NVIDIA GPU typeInstance type t1i.nanot1i.nanoVolume Root volume: 30Root volume: 30Key pair Select key pair Select key pair Network - VPC: tutorial
- Subnet:main
ㄴ Public subnet in kr-central-2-a
- Security Group:tutorial-nat-sg- VPC: tutorial
- Subnet:tutorial_{VPC_CODE}_sn_1(10.0.80.0/20)
ㄴ Public subnet in kr-central-2-b, select the subnet ending withsn_1
- Security Group:tutorial-nat-sg -
Verify all the input values and select [Create] to create the VM.
Step 4. Configure NAT instance
Assign public IP addresses to the two NAT instances (tutorial-nat-instance-a and tutorial-nat-instance-b) and proceed with the NAT configuration.
① tutorial-nat-instance-a
-
Go to Virtual Machine > Instance and select
tutorial-nat-instance-a. Select [Associate public IP]. -
In the public IP assignment popup, select Create new public IP and assign it automatically, then select [OK]. The attached public IP can be viewed in the Network tab.
-
Open a terminal on your local machine and navigate to the folder containing your key pair file using the
cdcommand:cd ~/Downloads
chmod 400 $(PRIVATE_KEY).pem
ssh -i $(PRIVATE_KEY).pem ubuntu@$(NAT_INSTANCE_PUBLIC_IP) -
Configure the NAT instance by running the following commands:
sudo apt-get update -y
LINE=$(grep 'net.ipv4.ip_forward=' /etc/sysctl.conf)
sudo sed -i "s/${LINE}/net.ipv4.ip_forward=1/" /etc/sysctl.conf
sudo sysctl -p
INTERFACE=$(ip link | awk -F: '$0 !~ "lo|vir|wl|^[^0-9]"{print $2;getline}')
sudo /sbin/iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o ${INTERFACE} -j MASQUERADE
sudo apt-get install -y iptables-persistent -
When prompted, press Yes to save the configuration.
-
If successful, the NAT instance setup will show the following confirmation screen:
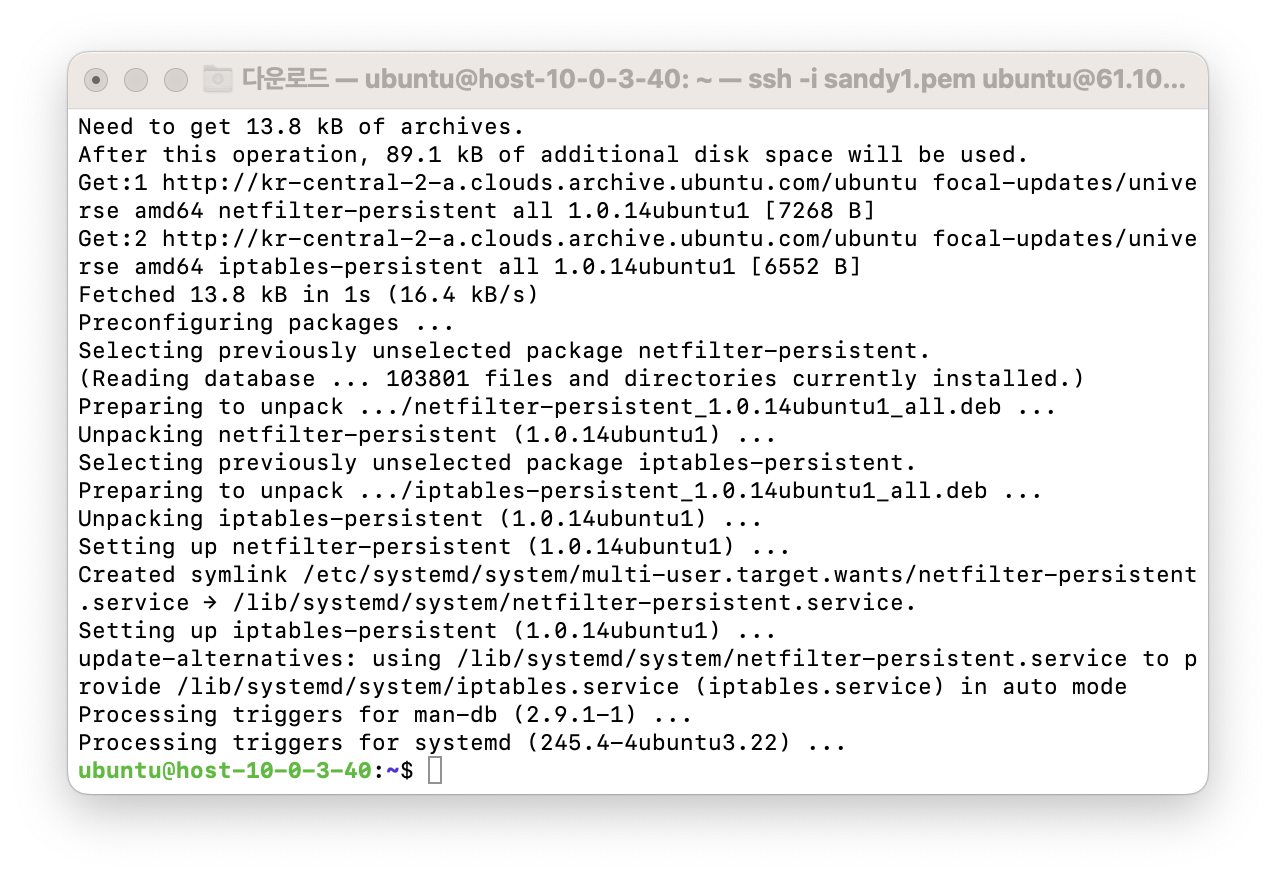
② tutorial-nat-instance-b
Follow the same steps as tutorial-nat-instance-a to configure tutorial-nat-instance-b.
By completing these steps, NAT instances are now deployed and configured in multiple availability zones. Private subnet instances can securely communicate with external networks through these NAT instances.
Step 5. Change source/destination check setting
By default, instances verify source and destination, allowing only traffic directed to their own IP address. However, NAT instances must handle traffic even if the source and destination are not their own.
You can configure instances for NAT use by modifying the source/destination checks setting.
-
Go to KakaoCloud console > Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine.
-
In the Instance menu, select
tutorial-nat-instance-a, select the More actions icon, and select Change source/destination checks. -
In the Change source/destination checks popup, select Disable and then select [Close]. (Default: Enabled)
infoThe default setting for Source/Destination Check is Enabled, which restricts network traffic to the instance's IP/MAC address for security. When set to Disabled, the instance can route traffic to and from other IP/MAC addresses according to the security group policy.
-
Repeat the same steps for
tutorial-nat-instance-b.
Step 6. Create and configure routing tables
Routing tables control the flow of network traffic in subnets. This step configures routing rules to ensure that outbound traffic from private subnets routes through the NAT instance in the respective availability zone.
-
Go to KakaoCloud console > Beyond Networking Service > VPC.
-
In the Routing table tab, select [Create Routing Table] and create routing tables for each availability zone as follows:
Configuration by Availability Zone kr-central-2-a kr-central-2-b Routing Table Name tutorial-priv-a-rttutorial-priv-b-rtVPC tutorialtutorial -
Select the created routing table to access its details.
-
In the Routes tab, select [+ Add Route].
-
For each availability zone, route traffic with a destination of
0.0.0.0/0to the NAT instance in that zone. The instance ID can be found in Virtual Machine > Instance.Routing Table Settings tutorial-priv-a-rt tutorial-priv-b-rt Target Type Instance Instance Target Instance {tutorial-nat-instance-a-id}{tutorial-nat-instance-b-id}Destination 0.0.0.0/00.0.0.0/0 -
In the Associations tab, select [+ Edit Associations] and associate the appropriate private subnets with each routing table.
Routing Table: tutorial-priv-a-rt
Verify and associate the following subnets:
Subnet IP CIDR Block Routing Table tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_510.0.64.0/20tutorial-priv-a-rt tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_410.0.48.0/20tutorial-priv-a-rt tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_310.0.32.0/20tutorial-priv-a-rt tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_210.0.16.0/20tutorial-priv-a-rt Routing Table: tutorial-priv-b-rt
Verify and associate the following subnets:
Subnet IP CIDR Block Routing Table tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_910.0.144.0/20tutorial-priv-b-rt tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_810.0.128.0/20tutorial-priv-b-rt tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_710.0.112.0/20tutorial-priv-b-rt tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_610.0.96.0/20tutorial-priv-b-rt
Step 7. Verify VPC topology
In the Topology tab of your VPC, verify that the network topology is configured correctly.
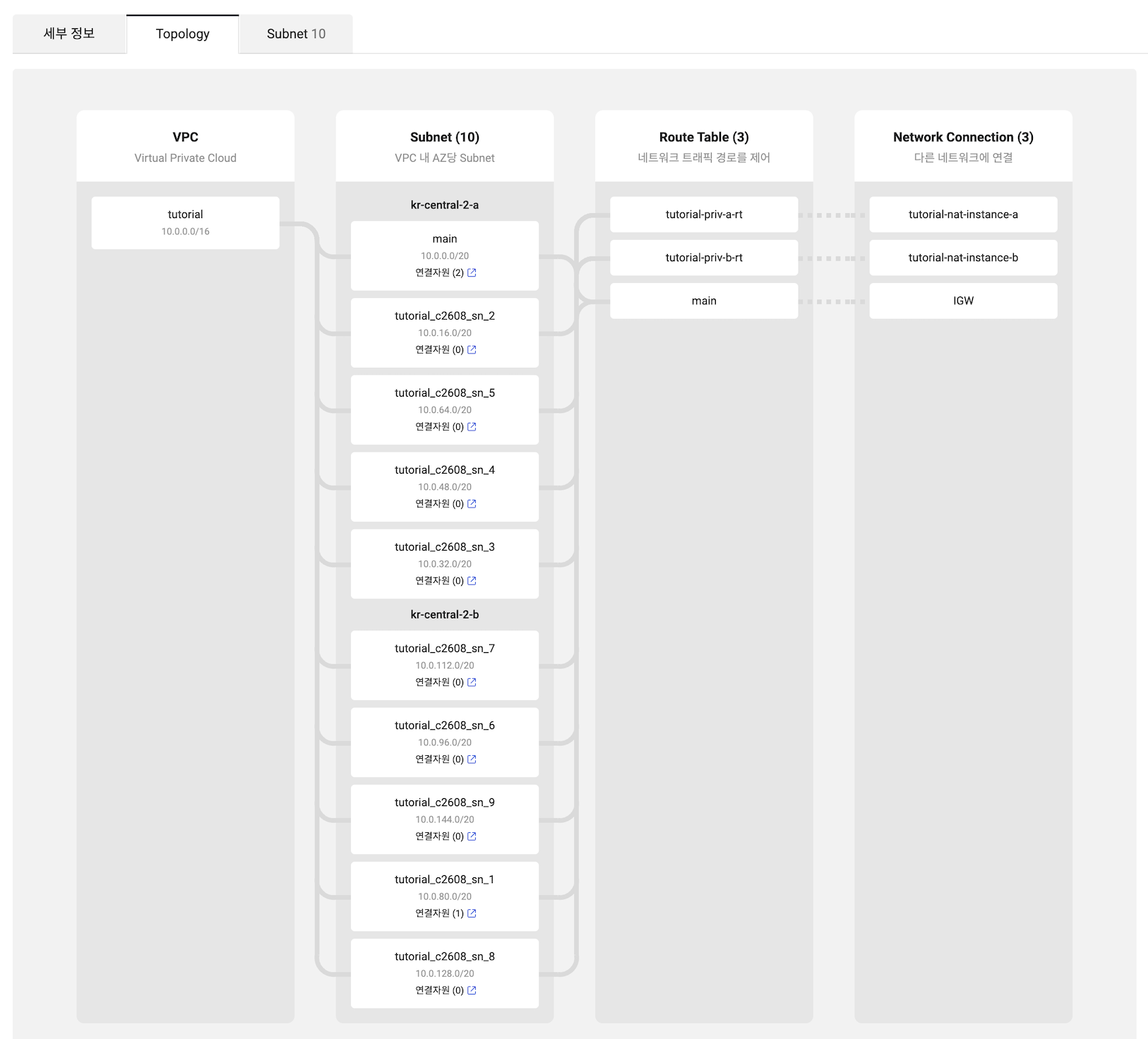
VPC topology verification
Verify results
To verify the results, create three VM instances in KakaoCloud, including a Bastion host. Then, check whether the public IPs used in private subnet instances match the public IPs of the NAT instances.
- The Bastion host serves as a gateway for secure access to internal resources.
Step 1. create security group for bastion instance
follow the steps below to create a security group for the bastion instance and configure Inbound rules.
-
Select VPC and go to Security Group.
-
Select the [Create security group] button.
-
In the create security group popup, enter
sg-bastionas the security group name. -
In the Inbound rules tab, add the following rules, then select the [create] button.
Check your public ipselect the button below to check your current public ip.
inbound rule protocol source port number bastion inbound policy 1 TCP {your public IP}/3210000-10010 bastion inbound policy 2 TCP {your public IP}/3281 bastion ssh policy TCP {your public IP}/3222 -
in the Outbound rules tab, add the following rules, then select the [create] button.
outbound rule protocol destination port number bastion outbound policy ALL 0.0.0.0/0 ALL
Step 2. create bastion instance
-
Go to Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine > Instance menu and select the [Create instance] button, then create the required bastion instance as listed below.
Item Description Basic information - Name: tutorial-bastion
- Quantity:1Image Ubuntu 20.04
⚠️ Select a standard image, not an NVIDIA typeInstance type t1i.nanoVolume Root volume: 30Key pair Use the existing key pair from previous tasks Network - VPC: tutorial
- Subnet:main
- Security group:sg-bastion(use as configured)
Step 3. create security group for private instance
-
Select the Security group tab in the VPC.
-
Select the [Create security group] button.
-
In the Create security group popup, enter
private-vm-sgas the security group name. -
In the Inbound rules tab, add the following rules and select the [Create] button.
- Traffic entering internal hosts is relayed through the bastion. Verify that the
az-a-vmandaz-b-vmhosts can receive traffic sent from the bastion in the KakaoCloud console security group. Ensure the following rules are included and added:
Inbound rule Protocol Source Port number private-vm inbound policy TCP {BASTION_PRIVATE_IP}/32
- Private IP oftutorial-bastion, available in Virtual Machine > Instance menu22 - Traffic entering internal hosts is relayed through the bastion. Verify that the
-
In the Outbound rules tab, add the following rules and select the [Create] button.
Outbound rule Protocol Destination Port number private-vm outbound policy ALL 0.0.0.0/0 ALL
Step 4. Create private instances by availability zone
-
Select the [Create instance] button in the Beyond Compute Service > Virtual Machine > Instance menu, and create VM instances in two availability zones as follows.
Availability zone settings kr-central-2-a kr-central-2-b Basic information - Name: az-a-vm
- Count:1- Name: az-b-vm
- Count:1Image Ubuntu 20.04
⚠️ Select a standard image, not NVIDIAUbuntu 20.04
⚠️ Select a standard image, not NVIDIAInstance type t1i.nanot1i.nanoVolume Root volume: 30Root volume: 30Key pair Use the existing key pair from the previous step Use the existing key pair from the previous step Network - VPC: tutorial
- Subnet:tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_2(10.0.16.0/20)
- Security group:private-vm-sg- VPC: tutorial
- Subnet:tutorial_{VPC_ID}_sn_6(10.0.96.0/20)
- Security group:private-vm-sg
Step 5. Associate public IP to bastion instance
- In the Virtual Machine > Instance menu, select the previously created
tutorial-bastioninstance and select the [Associate public IP] button. - In the public IP attachment popup, select Create new public IP and assign it automatically and select the [OK] button.
- The assigned public IP can be verified in the Network tab.
Step 6. Configure bastion host
-
Open a terminal in your local environment and navigate to the folder containing your key pair file using the
cdcommand. -
Run the following command to access SSH:
chmod 400 ${PRIVATE_KEY}.pem # grant read permission
ssh -i ${PRIVATE_KEY}.pem ubuntu@${BASTION_PUBLIC_IP}환경변수 설명 PRIVATE_KEY🖌︎ private key file name BASTION_PUBLIC_IP🖌︎ Virtual Machine > Instances tab, select the tutorial-bastioninstance, then check the Network tab for the public IPinfoIf a
bad permissionserror occurs due to private key file permission issues, use thesudocommand to resolve the problem. -
Configure Bastion host using nginx-proxy-manager by connecting to the Bastion host via SSH and running the following command for provisioning:
Configure Bastion hostsudo curl -o /tmp/init-bastion.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kakaoenterprise/kc-handson-config/vm-3tier/init-bastion.sh
bash /tmp/init-bastion.sh -
Open a browser in your local environment and access the management page using the following address:
- HTTP://
${BASTION_PUBLIC_IP}:81/login
- ID:
admin@example.com - Password:
changeme
- HTTP://
-
Go to Dashboard > Streams and register streams for each host (
az-a-vm,az-b-vm) by availability zone. The private IPs of each instance can be found in the Virtual Machine > Instance tab by selecting the respective instance and checking the Network tab.Setting by availability zone az-a-vm az-b-vm Incoming port 1000010001Forward host Private IP of az-a-vmPrivate IP of az-b-vmForward port 2222Forwarding protocol TCPTCP -
Move to the folder where the key pair file is downloaded, and check if you can access each host from your local environment using the port mappings.
Verify access by host* vm-a
ssh -i ${PRIVATE_KEY}.pem ubuntu@${BASTION_PUBLIC_IP} -p 10000
* vm-b
ssh -i ${PRIVATE_KEY}.pem ubuntu@${BASTION_PUBLIC_IP} -p 10001
Step 7. Verify IP match
Run the command below to check the public IP currently used for external communication. If this IP matches the public IP of the NAT instance, the previous steps were successfully completed. The public IP of the NAT instance can be found in the Virtual Machine > Instance menu by clicking on tutorial-nat-instance-a / tutorial-nat-instance-b and checking the Network tab.
curl https://ifconfig.me/ip
# Example result: ***.***.***.***