Key Concepts
Object
In Object Storage, all files are stored as objects in a key-value structure and are included in containers called buckets. Files are a subset of objects and correspond to the value part in the object structure, while the key serves as a unique identifier for accessing the file.
Object key
The object key is a unique identifier for the object and represents the file’s location within the bucket. For example, if a file named cloud.png is located in the i folder under the kakao folder in a bucket, the key is represented as kakao/i/cloud.png. The key must not exceed 432 bytes, including slashes (/) used to express directory structures. Requests that modify the key (e.g., uploads, renames, moves) may fail due to this limit.
Object Storage operates on a flat structure rather than a directory-based hierarchy. The use of / in keys is for user convenience only and does not imply actual directory layers. Internally, data is mapped directly to the key.
Object URL
To access a file (value) uploaded to a bucket, you must use a URL based on the object key.
The URL structure is: https://objectstorage.{region-name}.kakaocloud.com/v1/{project-ID}/{bucket-name}/{object-key}. You can find the URL of each file in the bucket details page. See Object details for more information.
URL structure
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| region-name | The name of the deployed region |
| project-ID | The ID of the deployed project |
| bucket-name | The name of the created bucket |
| object-key | The key of the uploaded object |
File management in console
You can manage files in a bucket using the web console. For more information, refer to the Object management guide.
Metadata
You can define metadata to describe objects. Metadata is categorized as system-defined metadata, which informs Object Storage systems, and user-defined metadata, which is freely set by users. See Set metadata for details.
Object tag
Tags allow you to classify objects using key-value pairs. Object tags can be used in lifecycle rules to manage the lifespan of objects. See Set object tag for more information.
Bucket
A bucket is a container that stores objects and serves as the unit for applying access control and lifecycle configurations. For more details, refer to Create and manage bucket.
Bucket type
Object Storage currently supports the Standard bucket type. Standard buckets offer high durability and availability, making them ideal for frequently accessed data.
Lifecycle
Lifecycle policies can automatically delete or move files to another bucket type after a specified time. Moving to another bucket type will be supported in a future update.
Bucket visibility
You can allow public access to a bucket, enabling anyone to read its contents. When public access is enabled, access is read-only. See Manage bucket permissions for more information.
File uploads and modifications are only available through the console or API.
Stability and scalability
Object Storage has no limit on the number of objects or capacity per bucket. It ensures stability by distributing or replicating data across different hardware. Unlike hierarchical block storage, Object Storage uses a flat key-value structure for scalability.
You can add files without limitation or configuration. Since all data is stored in a flat namespace, there is no latency caused by directory depth, and access is consistent regardless of the number of files in a bucket.
Role and permission
IAM roles
In IAM, roles such as Project Admin, Member, Viewer, Object Storage Manager, and Object Storage Viewer initially only have permissions for creating and listing buckets. However, once a bucket is created, the Object Storage roles are assigned to the bucket based on the Initial role assignment on bucket creation.
| Permission | Project Admin | Project Member | Project Reader | Object Storage Manager | Object Storage Viewer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Create bucket | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| View bucket | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Permissions for editing and deleting buckets are based on the Object Storage roles assigned to the bucket.
Initial role assignment on bucket creation
When a bucket is created, the following roles are assigned by default:
| IAM role | Object Storage role |
|---|---|
| Project Admin | storage.admin |
| Project Member | storage.editor |
| Project Reader | storage.viewer |
| Object Storage manager | storage.editor |
| Object Storage viewer | storage.viewer |
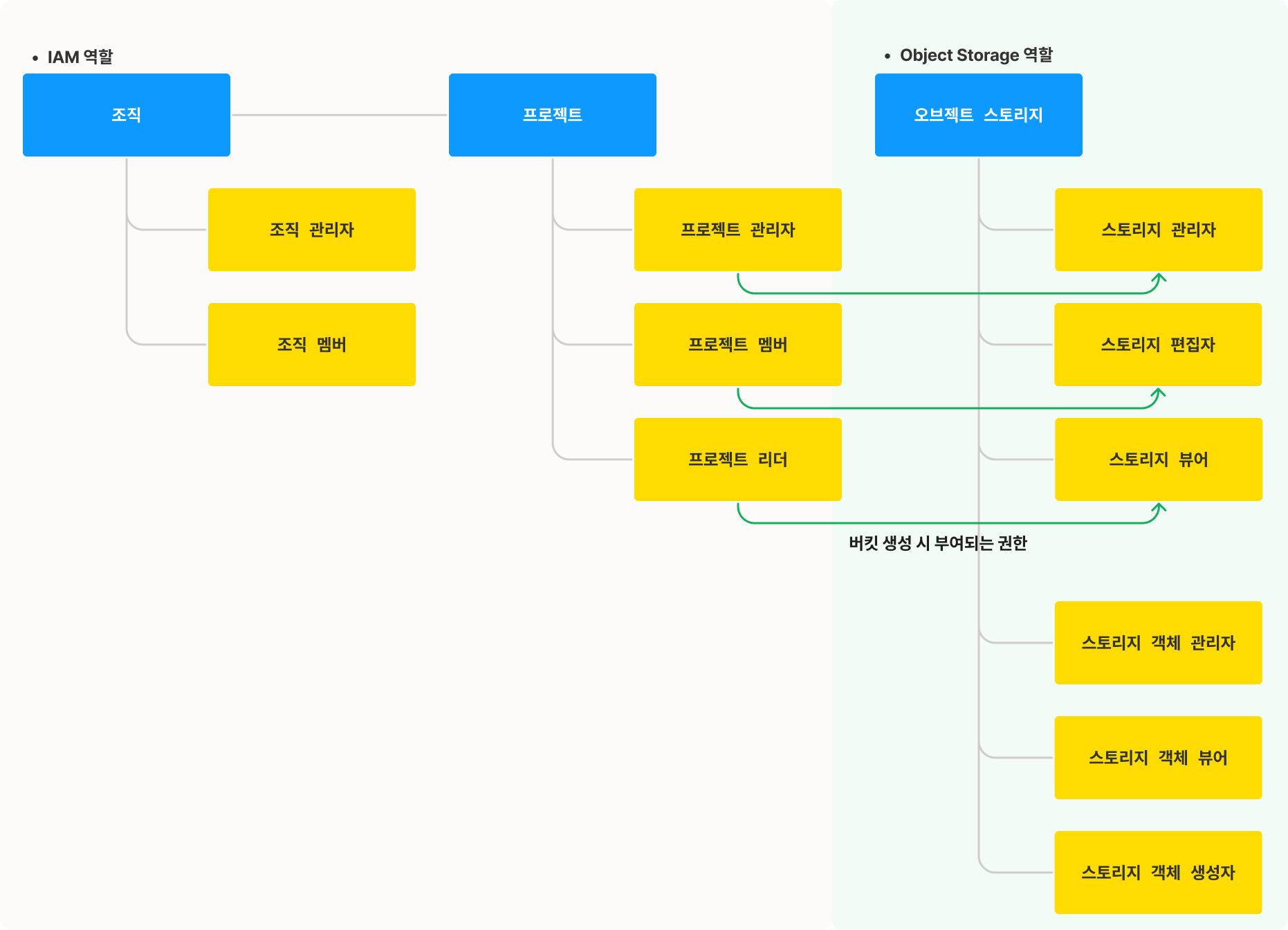 Permission architecture
Permission architecture
Bucket permissions by Object Storage role
Object Storage roles determine permissions for managing buckets and objects. The following tables show the permissions by role.
- Standard bucket
- Classic bucket
| Permission scope | Role | Permissions | S3 Bucket ACL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bucket | Storage admin (storage.admin) | Full permission to manage both buckets and objects - storage.buckets.delete - storage.buckets.get - storage.buckets.update - storage.buckets.getIamPolicy - storage.buckets.setIamPolicy - storage.objects.create - storage.objects.delete - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get - storage.objects.update | FULL_CONTROL |
| Storage editor (storage.editor) | Permissions to manage buckets and objects except bucket IAM policy - storage.buckets.get - storage.buckets.update - storage.objects.create - storage.objects.delete - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get - storage.objects.update | READ + WRITE | |
| Storage viewer (storage.viewer) | Permission to view bucket and object metadata - storage.buckets.get - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get | READ | |
| Object admin (storage.objectAdmin) | Full control over objects (list/create/view/delete) - storage.objects.create - storage.objects.delete - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get - storage.objects.update | READ + WRITE | |
| Object reader (storage.objectReader) | Permission to list/view object metadata (no IAM policy access) - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get | READ | |
| Object creator (storage.objectCreator) | Permission to create objects only - storage.objects.create | WRITE | |
| Bucket owner (storage.owner) | Manage IAM and metadata (excluding creation) - storage.buckets.delete - storage.buckets.get - storage.buckets.update - storage.buckets.getIamPolicy - storage.buckets.setIamPolicy - storage.objects.create - storage.objects.delete - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get - storage.objects.update | FULL_CONTROL | |
| Bucket policy editor (storage.policyEditor) | Manage bucket IAM and objects (excluding creation/deletion) - storage.buckets.get - storage.buckets.update - storage.buckets.getIamPolicy - storage.buckets.setIamPolicy - storage.objects.create - storage.objects.delete - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get - storage.objects.update | FULL_CONTROL | |
| Policy reader (storage.policyReader) | Permission to read bucket IAM policy - storage.buckets.getIamPolicy | READ_ACP | |
| Policy writer (storage.policyWriter) | Permission to add/remove IAM policies (not read) - storage.buckets.setIamPolicy | WRITE_ACP |
| Permission scope | Role | Permissions |
|---|---|---|
| Bucket | Storage admin (storage.admin) | Full permission to manage both buckets and objects - storage.buckets.delete - storage.buckets.get - storage.buckets.update - storage.buckets.getIamPolicy - storage.buckets.setIamPolicy - storage.objects.create - storage.objects.delete - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get - storage.objects.update |
| Storage editor (storage.editor) | Permissions to manage buckets and objects except IAM - storage.buckets.get - storage.buckets.update - storage.objects.create - storage.objects.delete - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get - storage.objects.update | |
| Storage viewer (storage.viewer) | Permission to view metadata of buckets and objects - storage.buckets.get - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get | |
| Object admin (storage.objectAdmin) | Full object control - storage.objects.create - storage.objects.delete - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get - storage.objects.update | |
| Object reader (storage.objectReader) | List and view object metadata - storage.objects.list - storage.objects.get | |
| Object creator (storage.objectCreator) | Only permission to create objects - storage.objects.create |
Role types
Object Storage role types include:
| Role type | Description |
|---|---|
| User | A single user assigned a role |
| Group | Type of AllUserGroup (all users, regardless of authentication status) |
| Service account | An account created by the user for API calls - Not an actual IAM user - Used for issuing authentication tokens |
| Role group | Group assigned by IAM role - Project Admin - Project member - Project Reader - Object Storage manager - Object Storage viewer |
If you assign a role with Write permissions to AllUserGroup, any unauthenticated or anonymous user will be able to upload, modify, or delete objects in the bucket.
You can check whether the role includes Write permissions in Role-based Permissions.
Permission-specific functions
The following table summarizes functions available per permission scope.
| Scope | Permission | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Bucket | storage.buckets.create | Create bucket |
| storage.buckets.delete | Delete bucket | |
| storage.buckets.list | List buckets, view metadata | |
| storage.buckets.get | View bucket details, metadata | |
| storage.buckets.update | Update bucket, set acccess logging - e.g., modify metadata | |
| storage.buckets.getIamPolicy | View IAM policy, lifecycle policy | |
| storage.buckets.setIamPolicy | Add/update/delete IAM policy, configure lifecycle | |
| Object | storage.objects.create | Create object - e.g., upload file, create folder |
| storage.objects.delete | Delete object | |
| storage.objects.list | View object list/metadata | |
| storage.objects.get | View object details - e.g., metadata, tags, file info, download | |
| storage.objects.update | Update object - e.g., modify metadata or tags, rename |